Open Targets Platform 22.06 has been released!
The latest release of the Platform — 22.06 — is now available at platform.opentargets.org.
Key points
- We have included five additional studies in our Gene Burden widget, incorporating evidence from a number of different therapeutic areas
- The term “medical procedure” has been added to our ontology
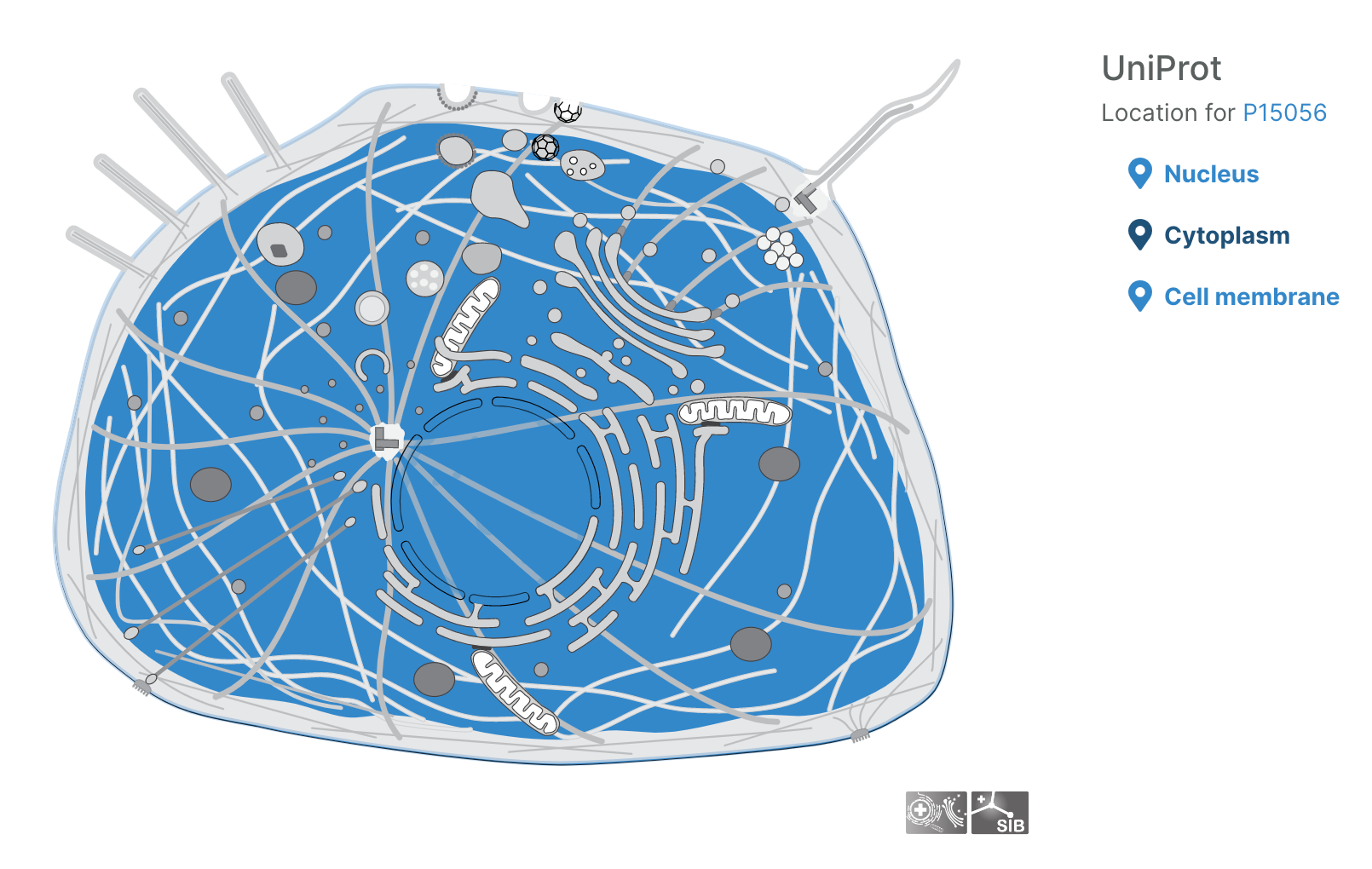
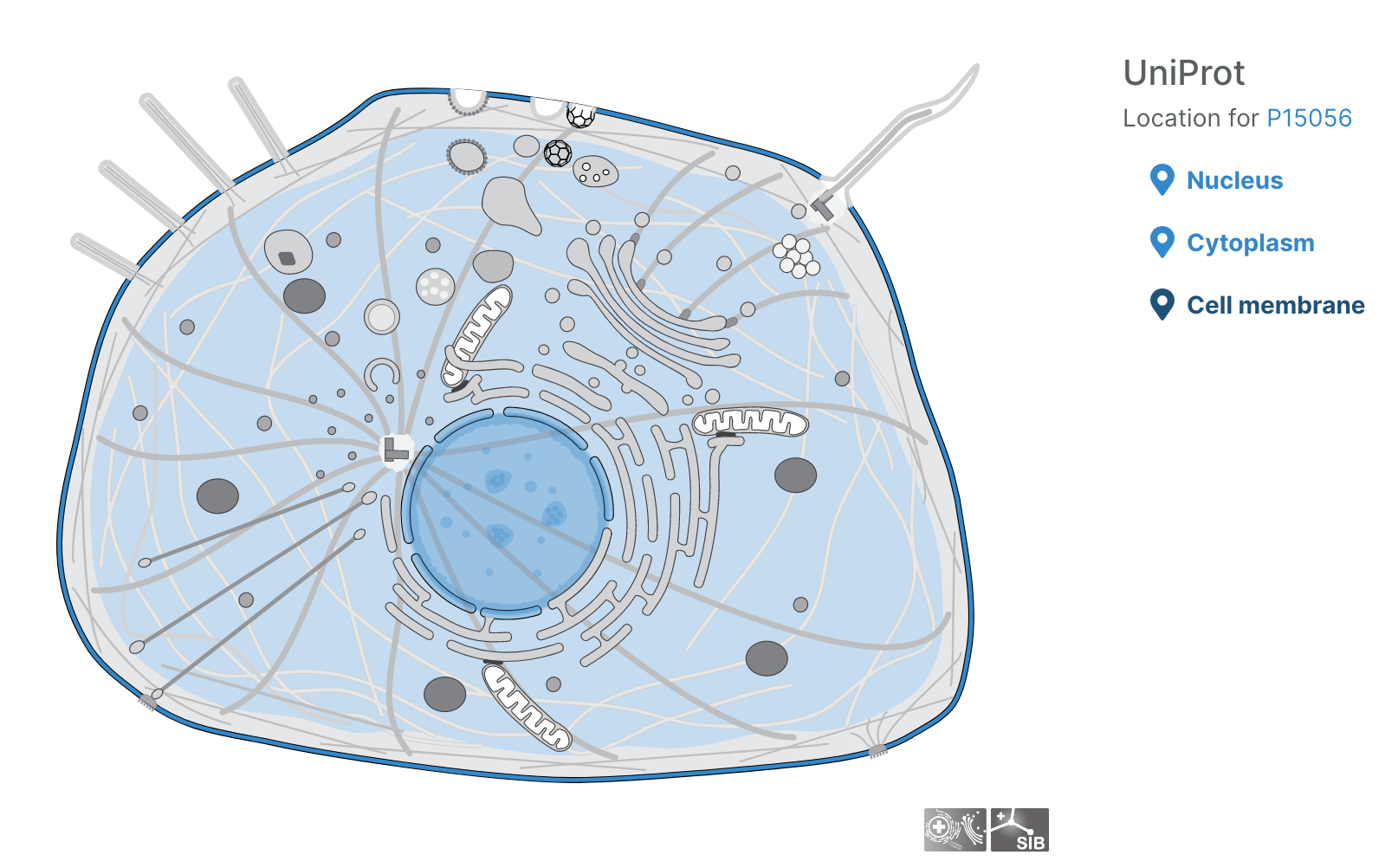
- Users can now visualise subcellular locations of targets
Key stats
| Metric | Count |
|---|---|
| Targets | 61,524 |
| Diseases | 23,074 |
| Drugs | 12,854 |
| Evidence strings | 14,455,104 |
| Associations | 7,247,865 |
Take a look at the Open Targets Community for more detailed stats.
Additional gene burden evidence
Our previous release (22.04) featured the addition of a new evidence source for gene burden, incorporating the results from the aggregation of rare and ultra-rare variants at the gene-level available in AstraZeneca’s PheWAS portal and Backman et al..
To this, we have now added results from five additional studies, notably Genebass.
These bring in 1,465 new target-disease associations.
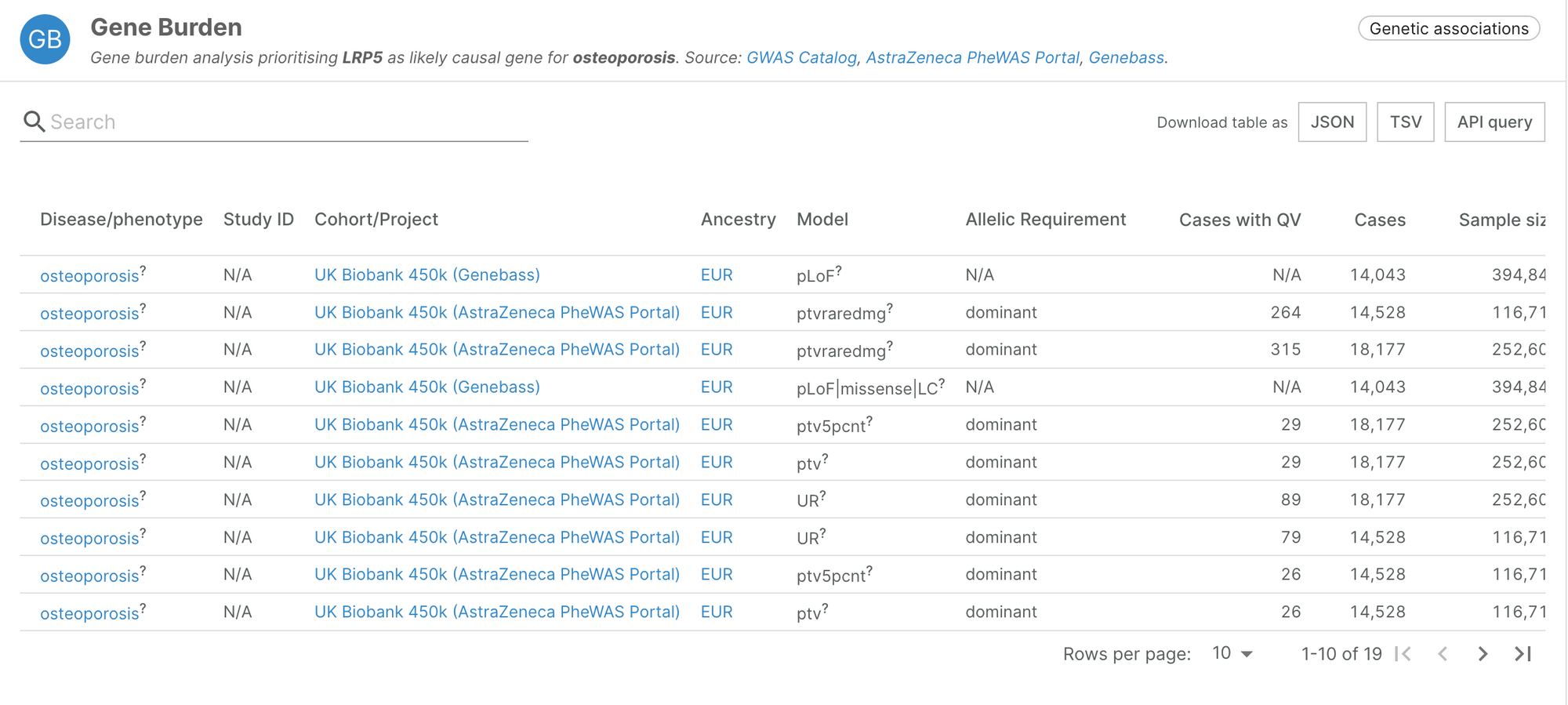
Genebass
Gene-based Association Summary Statistics (Genebass) is a resource of exome-based association statistics based on data available in the UK Biobank.
We have incorporated the results from their latest release, bringing in evidence supporting 7,238 associations, from 8,808 evidence strings, for 715 traits and 2,645 targets.
The evidence integrated from Genebass recapitulates known associations such as the link between PCSK9 and hypercholesterolemia, or LRP5 and osteoporosis.
It also includes novel associations, such as SCRIB and white matter microstructure measurement, highlighted by the authors in their recent manuscript (Karczewski, et al., 2022).
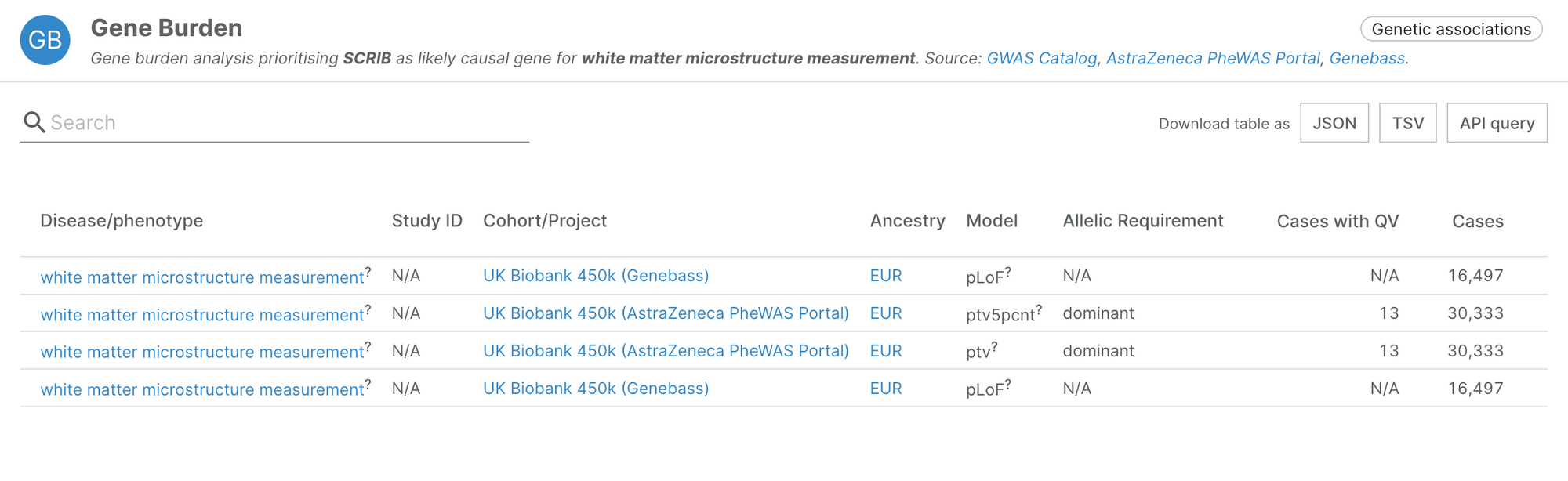
The additional studies we have integrated are:
- Bomba et al. (2022), the results of an Open Targets project which found associations between rare coding variants and blood metabolites

- Singh et al. (2022), a whole exome sequencing analysis of individuals with schizophrenia
- Satterstrom, Kosmicki, Wang et al. (2020), which identifies 102 genes which confer risk for Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Epi25 Collaborative (2019), which found that compared to controls, individuals with any type of epilepsy carried ultra-rare, deleterious mutations in constrained genes and in genes previously associated with epilepsy.
Find out more about how we integrated these studies in the Platform documentation.
Medical procedures added in the ontology
We have added evidence associating genes with medical procedures. This allows us to associate targets with such terms, mainly based on GWAS through the Open Targets Genetics portal, UK Biobank burden tests, and literature mining evidence.
In this way, Platform users can leverage genetic signals associated with a medical procedure to prioritise targets for a primary disease.
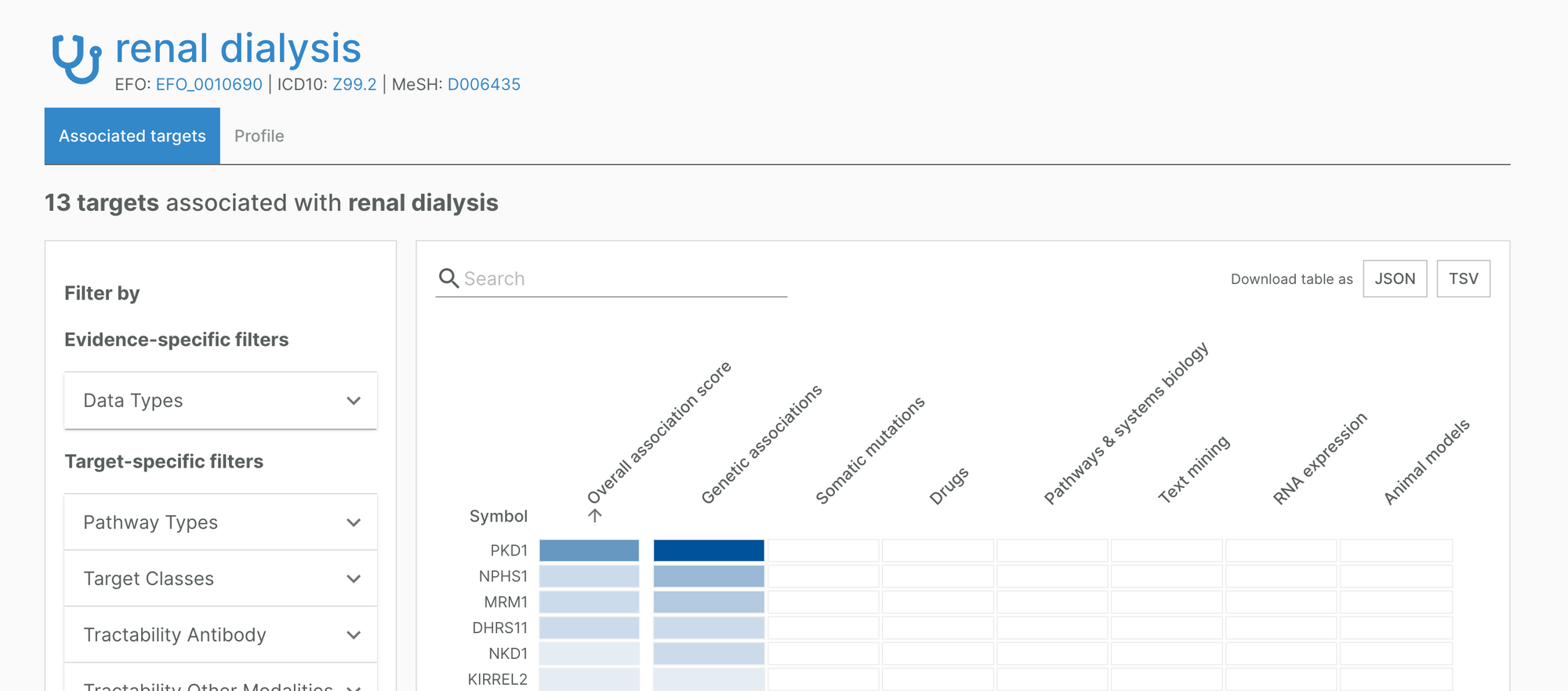
For example, the Platform now includes an association between renal dialysis and PKD1, a target strongly linked to kidney disease.
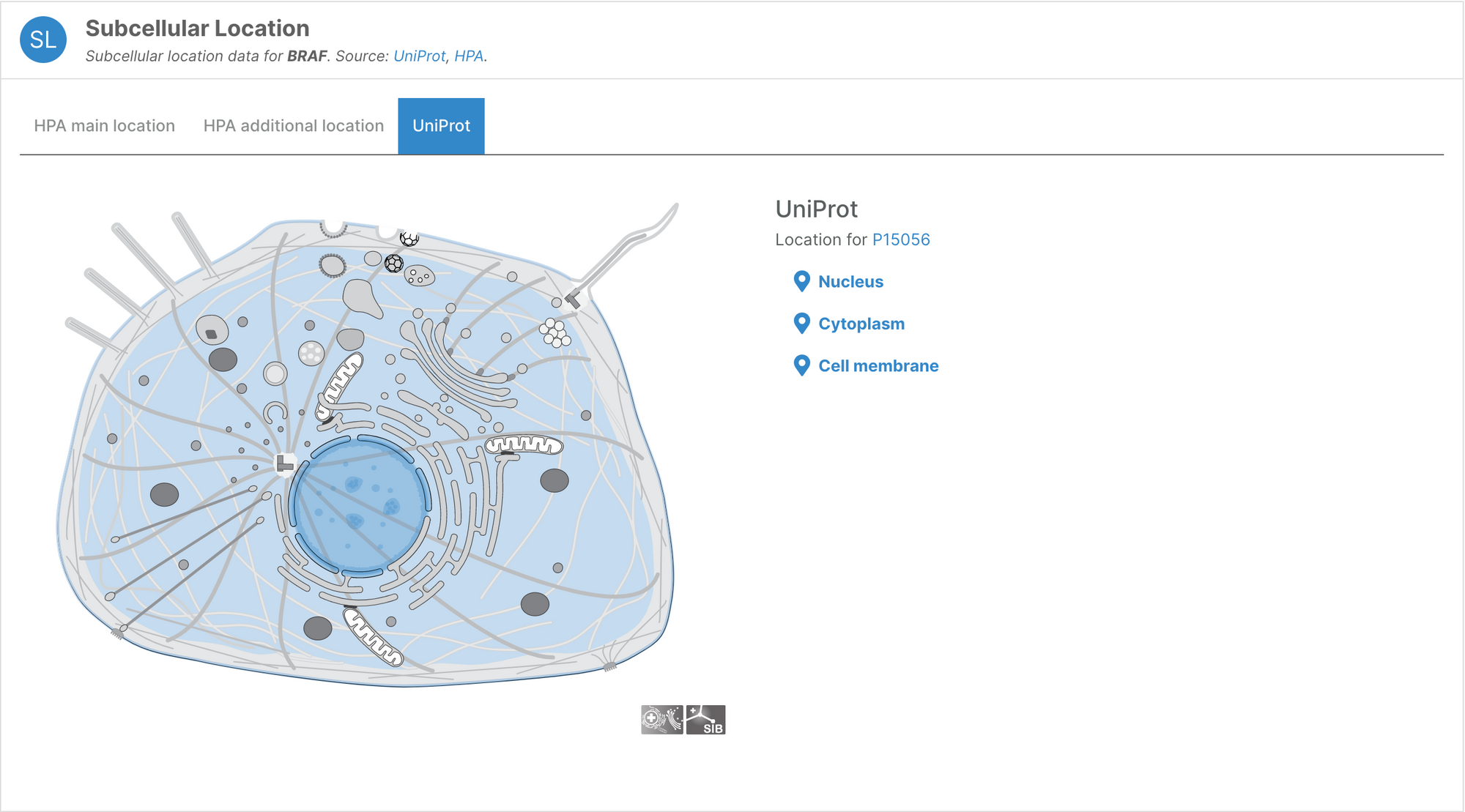
Subcellular locations visualisation
Users can now visualise the subcellular location of targets in the Platform using SwissBioPics visualisations.
Questions, thoughts, or comments? Let us know on the Open Targets Community!