Open Targets Platform 25.03 has been released!
The latest release of the Platform — 25.03 — is now available at platform.opentargets.org, and it’s a big one!
This release brings variant, study, and credible set information into the Open Targets Platform, effectively uniting the Open Targets Platform and Open Targets Genetics into a one-stop shop for human genetic and target discovery information. The data and analyses are also available through our API and data downloads options.
The expanded Platform retains all of the existing data and functionalities, but now includes detailed information about disease-causing variants and their gene predictions based on our in-house Locus-to-Gene machine learning model (L2G, find out more), allowing you to better explore and connect genetic data. You can interpret gene-disease evidence from both common and rare variation in one interface, and in multiple ancestries.
"Our new release is the result of two years of collaboration across the Open Targets partnership, aiming to centralise, standardise, and re-analyse publicly available studies," says David Ochoa, Open Targets Platform Coordinator.
"The new toolset will unblock faster iteration grounded on a solid scientific foundation and scalable open-source pipelines, setting up our informatics ecosystem for future challenges."
Read about our decision to merge the two platforms in the accompanying blog post.
This data release supersedes the last Open Targets Genetics release with significant updates for statistical genetic analyses. Please note that we no longer maintain Open Targets Genetics, and the web interface will soon be deprecated. If you have concerns or comments about this, please reach out to us on the Open Targets Community.
Key points
- The Platform now has three new entities: credible sets, studies, and variants. You can directly search for studies and variants from the search bar.
- GWAS credible sets provide evidence for target-disease associations. We previously sourced this data from Open Targets Genetics; you can now dig into the analyses directly in the Platform.
We also have a number of regular data updates, of note:
- We have filtered out Phase IV clinical trial evidence that lacks regulatory approval for the specific indication from our target-disease association data.
We have also made improvements to the web interface, with new colours, sorting, and visualisations.
For the full list of updates, take a look at the release notes.
Key stats
| Metric | Count |
|---|---|
| Targets | 78,766 |
| Diseases | 28,513 |
| Drugs | 18,081 |
| Evidence | 28,168,992 |
| Associations | 10,162,821 |
| Variants | 6,493,882 |
| Credible sets: | |
| gwas | 577,471 |
| sqtl | 223,507 |
| pqtl | 33,737 |
| tuqtl | 384,937 |
| eqtl | 1,349,700 |
| sceqtl | 52,746 |
| Unique studies assigned to GWAS credible sets | 35,744 |
| Tissues/cell-types from molQTL credible sets | 98 |
| Unique gene-study pairs with L2G>=0.5 | 437,338 |
| Unique gene-disease direct associations | 39,2784 |
| Unique diseases/traits covered by gene-disease direct associations | 7,462 |
New entity pages to dive into genetic data
We have merged the Open Targets Platform and Open Targets Genetics into a single target discovery Platform, providing a deeper integration between the GWAS and functional genomics previously in Open Targets Genetics, and the target identification and prioritisation tools available in the Open Targets Platform.
Practically, the Platform now has three additional interconnected entities: credible sets, studies, and variants. These new pages allow you to dig deeper into the GWAS evidence for a target-disease association, explore our analyses of GWAS and molecular QTL studies, and relevant annotation data. You can directly search for studies and variants from the Platform search bar.
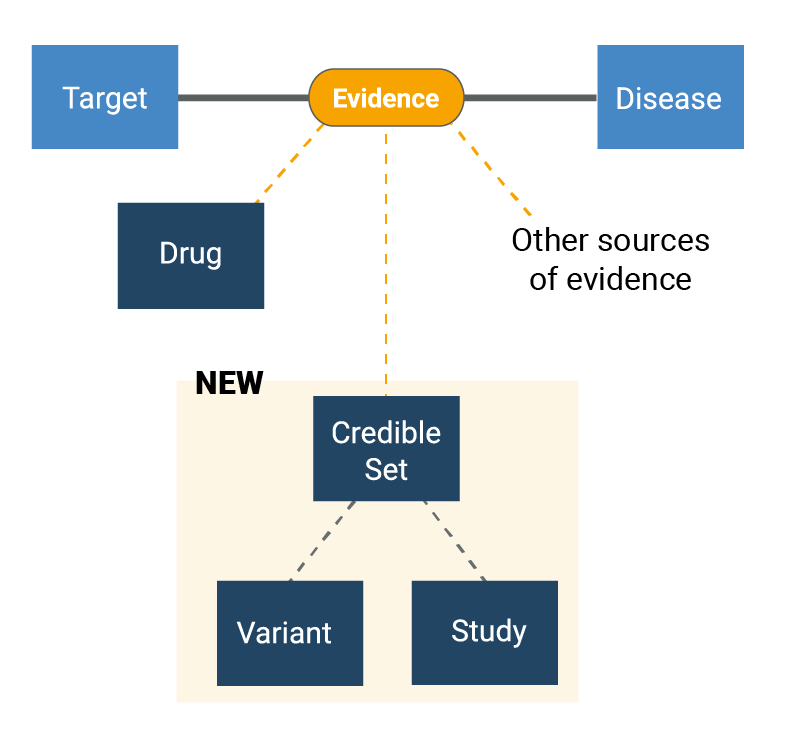
In a target-disease association page, the “Open Targets Genetics” column of evidence and accompanying widgets have been renamed “GWAS associations”. These list 95% GWAS credible sets prioritising the target as a likely causal gene for the disease. We have credible set analysis results for 393,000 direct gene-disease associations from GWAS credible sets (>20% more than in the last update of Open Targets Genetics).
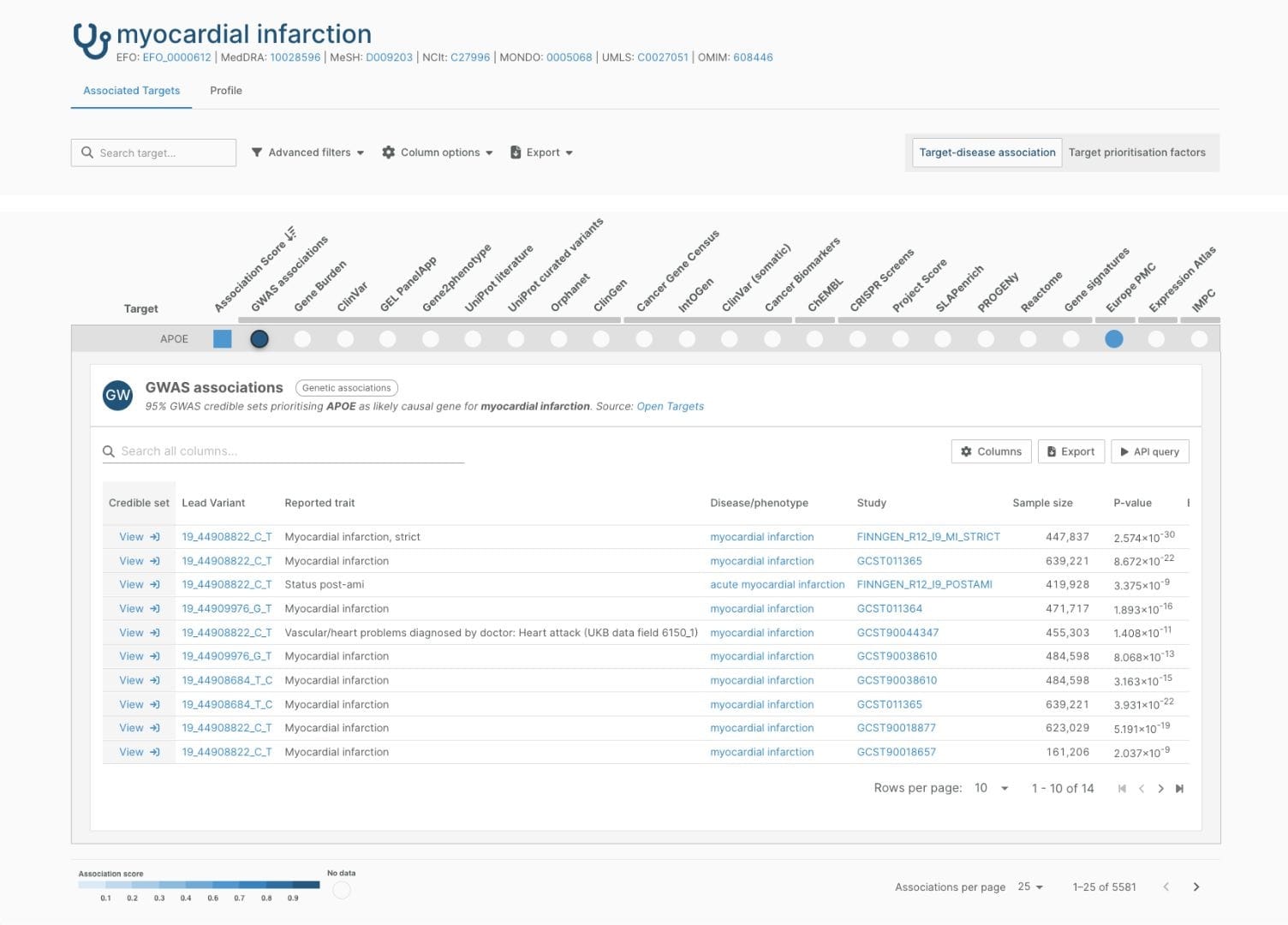
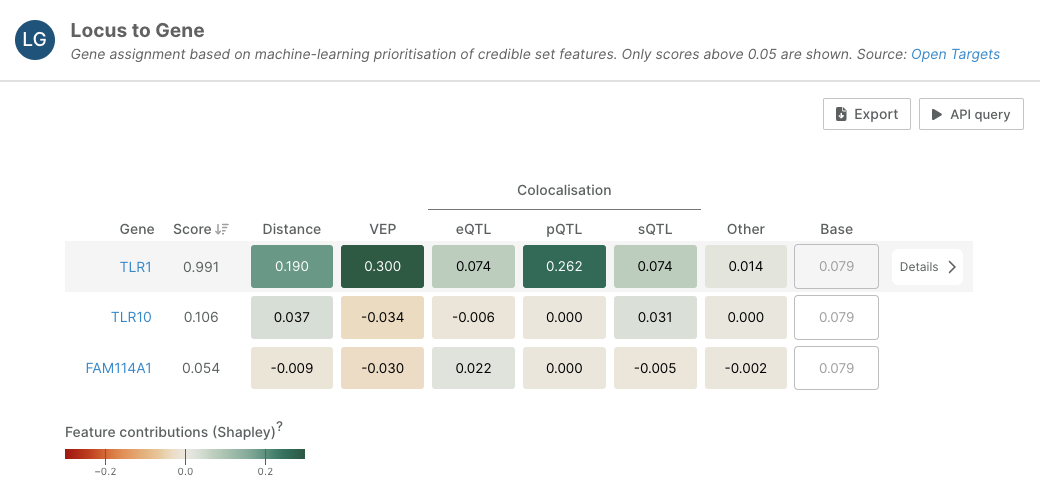
Each row in the widget represents a credible set — a set of variants near a genetic association signal that have a 95% probability of containing the true causal variant(s) for that signal — and you can now navigate to the credible set page to explore it in more detail.
Credible set pages
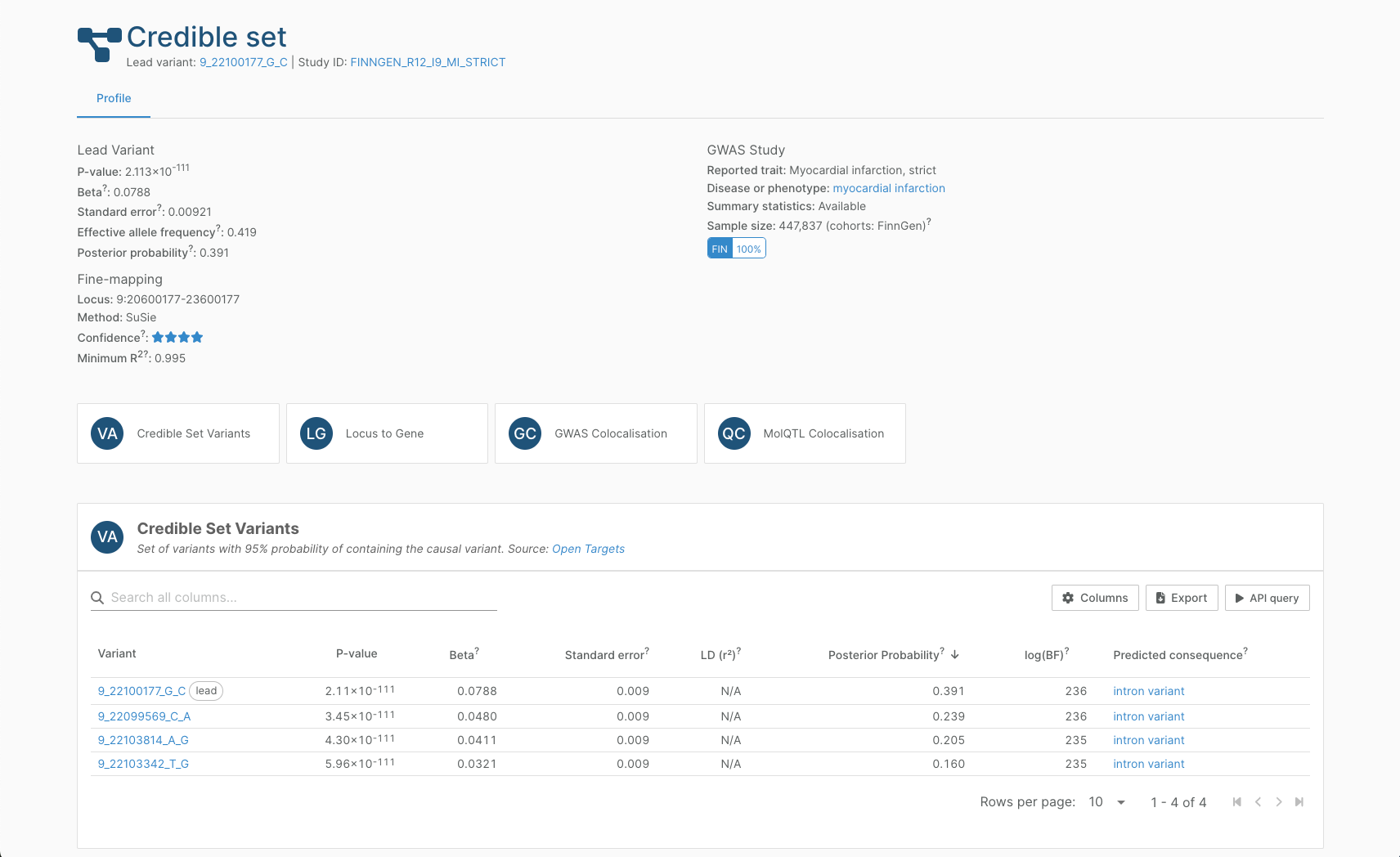
Our fine-mapping of 96,000 GWAS and molecular QTL studies result in 2.6 million credible sets derived from the GWAS Catalog, the eQTL Catalogue, FinnGen, and proteomics from the UK Biobank Pharma Proteomics Project.
We use four pipelines for fine-mapping, depending on the availability of summary statistics and appropriate population structure information. We have implemented a fine-mapping confidence rating for credible sets based on this analysis.
On the credible set page, you can look through:
- The list of variants in the credible set
- The list of likely causal genes from our Locus-to-Gene analysis
- Colocalisation results of overlapping sets from GWAS or molecular QTL studies which, respectively, can indicate other complex traits that may be related to the one of interest, and the likely functional consequence of the credible set.
Our colocalisation strategy
We undertake an All GWAS vs All GWAS and all GWAS vs All molQTL study comparison. This systematic data analysis enables you to view new studies in the context of all previously established GWAS and QTL information.
We use two different colocalisation methods (eCAVIAR and COLOC) depending on our statistical confidence in the fine-mapped credible set.
Study pages
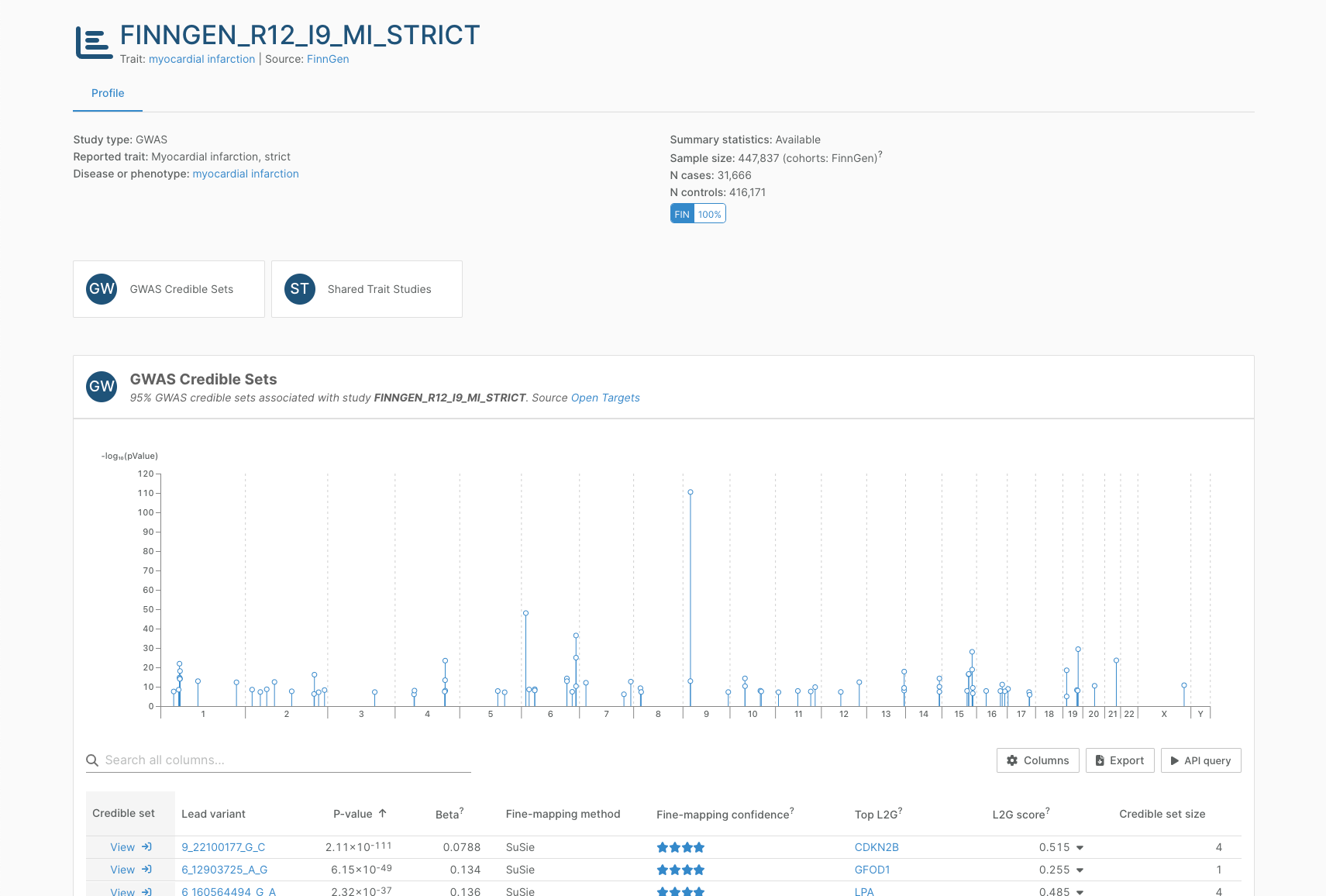
Each GWAS and molQTL study in the Platform has its own page, which enriches annotation information from the original sources such as the GWAS Catalog with additional metadata and quality control metrics.
We include binary and quantitative traits from the GWAS Catalog and FinnGen (R12), and QTL studies (scQTL, eQTL, sQTL, pQTL, and more) from the eQTL Catalogue and the UK Biobank Pharma Proteomics Project. All of our data is up to date as of Q1 2025.
Studies with and without summary statistics are processed and flagged accordingly. When possible, we perform quality control before ingestion for all studies to ensure they fulfil the minimum standards.
Variant pages
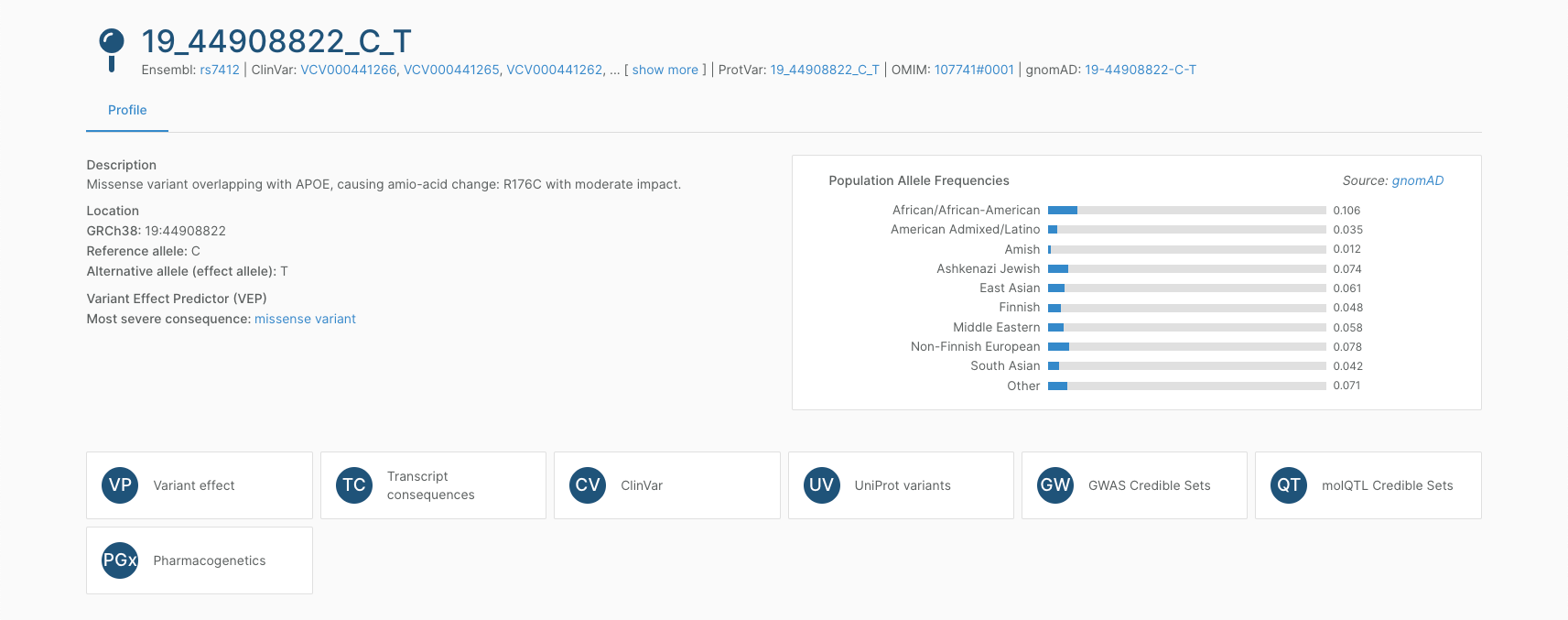
Finally, you can search for individual variants. The Platform provides functional context for 6.5 million rare and common variants connected with phenotype information and reported in at least one of our variant-to-phenotype sources. This includes L2G, rare disease clinical annotations, and pharmacogenetics annotations.
The variant page provides an overarching description of the likely consequence of a variant, as well as population allele frequencies. You can explore information on:
- Variant effect, with a visual summary of the predictions from different in silico methods of whether the variant is likely benign or deleterious,
- Nearby genes, to help understand the relationship between the variant and genes in the same region including distance genes, as well as the predicted consequence for each coding and non-coding canonical transcript in the region. For missense variants, you can also view the amino acid consequence for the respective UniProt protein.
- Associated phenotypes, across rare and common traits/diseases and drug response information. This includes GWAS credible sets, molQTL credible sets, ClinVar clinical submissions, Uniprot curated variants, and pharmacogenetics annotations from PharmGKB.
The new pages and data sources are fully described in our documentation: platform-docs.opentargets.org.
A completely new genetic analysis pipeline
We rebuilt our analysis pipeline from scratch. This means that there are a few notable differences between the data in this Platform release and the last release of Open Targets Genetics:
- We now only integrate variants that are associated with a disease, trait, or phenotype, for a total of 6.5M variants.
- The pipelines underpinning our genetic analyses have been completely rewritten as a Python package for post-GWAS analysis: Gentropy. The Gentropy toolkit encompasses all pipelines for Locus-to-Gene prediction, and is optimised for scalable and reproducible analysis.
- Colocalisation is now based on credible set overlaps.
- Our Locus-to-Gene (L2G) machine learning model prioritises likely causal genes at each GWAS locus by using functional genomics features. Predictions are obtained by applying a pre-trained model to all rows in the feature matrix. We have now included Shapley values to our L2G predictions to illustrate the relative contribution of each feature to the overall score. Read more on this in the documentation.
Data updates
This release also includes a number of data updates, such as:
- A substantial increase in literature evidence thanks to improvements to our disambiguation of entities
- Updated gene burden data through FinnGen R12
- Updated data from Chemical Probes and Probes&Drugs resulting in 62 new unique compounds, and information for 27 targets not previously covered
For the full list of updates, please see the release notes.
Refined extraction of information from drug approvals
We have filtered out Phase IV clinical trial evidence that lacks regulatory approval for the specific indication from our target-disease association data.
Users reported that the way we previously integrated data from ChEMBL created some spurious associations from Phase IV trials, in cases where approved drugs are studied for new indications but did not demonstrate efficacy, or where drugs are used as adjunctive therapy or for symptom management rather than for treating the primary condition (for example lidocaine and colorectal cancer).
Improvements to the web interface
- We’ve improved the filtering and sorting of entities on our associations pages. In particular, there are now separate sections for uploaded entity lists and pinned entities, and you can remove individual filters from the view.
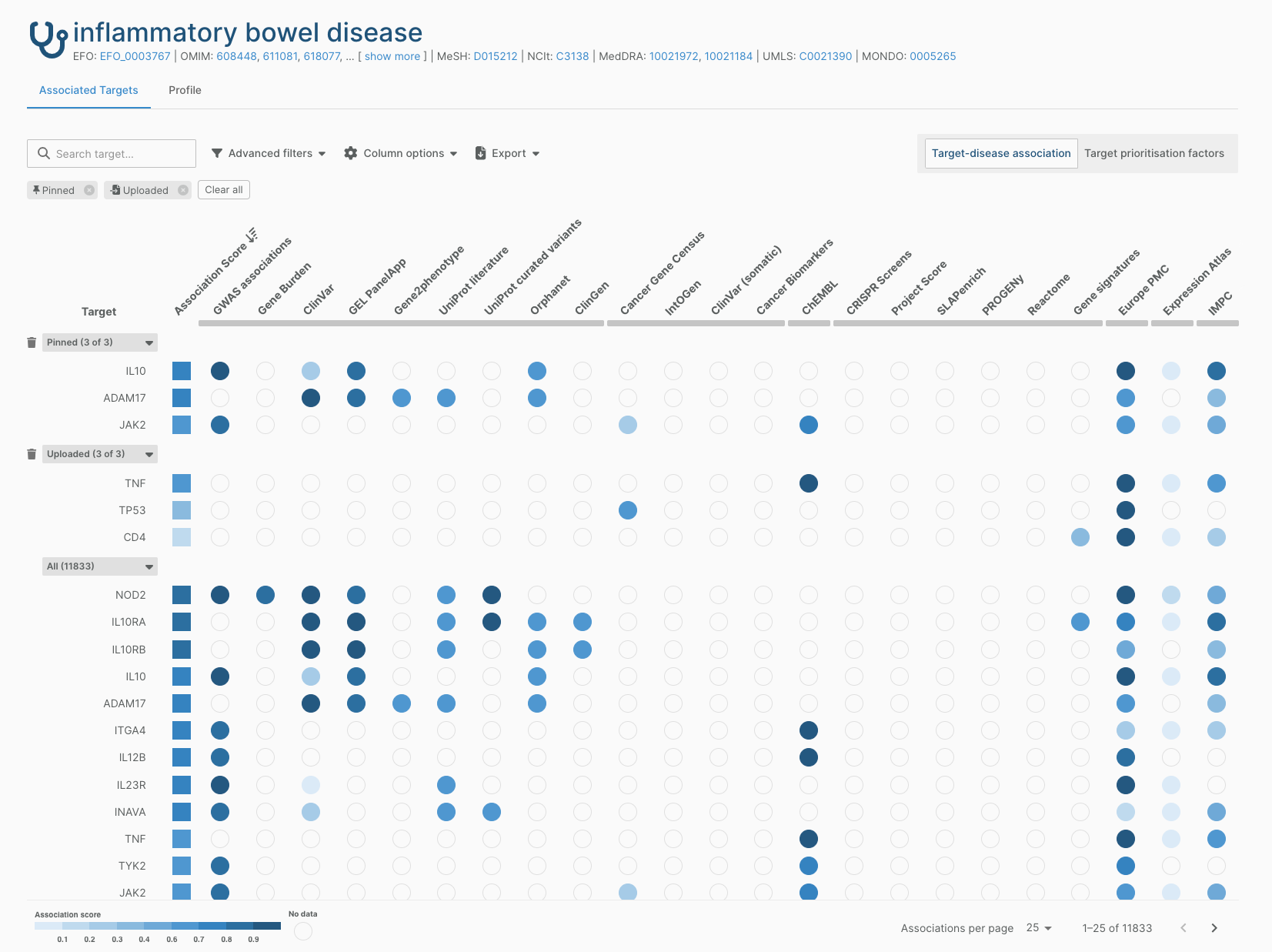
- Our Target Prioritisation view has a more accessible colour scheme.

- You can now select which columns you’d like to see within a widget; this makes it easier to export only the data that you are interested in.
- Our data downloads page has a more detailed description of each file. Note that we have temporarily removed the schemas, while we work to improve user access to our data downloads. You can expect to see additional changes in future releases!
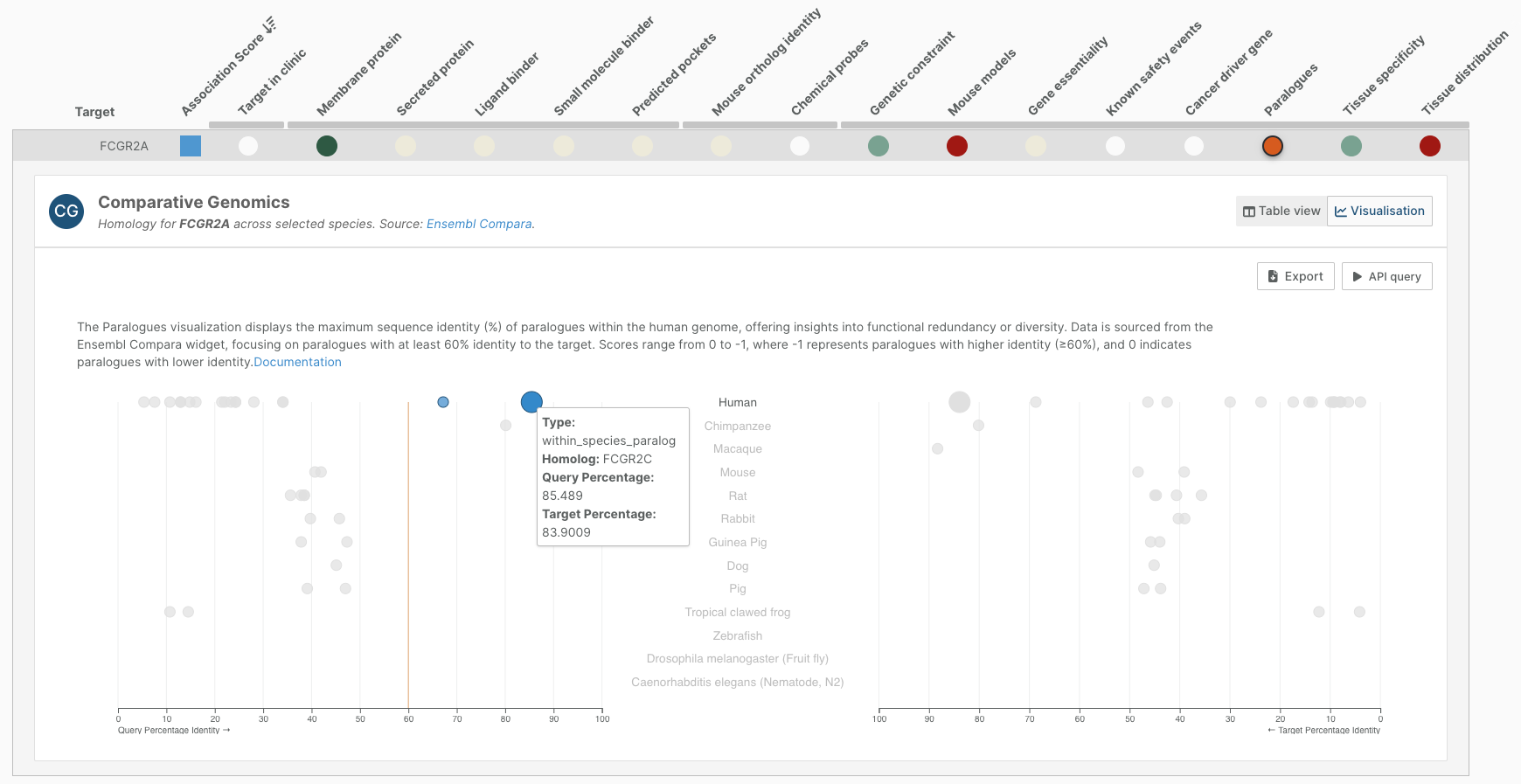
- We are working on new visualisations for the data in the Platform, several of which you can see in the new entity pages. We have also created a visualisation for orthologue data in our target prioritisation view.
We'd love to hear what you think of this update! Please share any comments or questions you have on the Open Targets Community.