Open Targets Platform 24.09 has been released!
The latest release of the Platform — 24.09 — is now available at platform.opentargets.org.
Please note, this will be the last release of the year. We are working on major updates to the Platform web interface, which we will share with you in our March 2025 release (25.03). See you there!
Key points
In addition to our regular data updates:
- Target phenotypes routinely tested in secondary pharmacology screening now part of our safety assessments
- FinnGen burden curation added to gene burden evidence
- Filters added to our target-disease associations pages so that users can customise the list of results
- Open Targets data is now available through Microsoft Azure Open Datasets
- OpenAI model used for literature summarisation has been updated
- Gene essentiality data from DepMap has a new visualisation
This release also deprecates the Classic Associations view.
Key stats
| Metric | Count |
|---|---|
| Targets | 63,121 |
| Diseases | 28,327 |
| Drugs | 18,041 |
| Evidence | 17,853,184 |
| Associations | 8,155,988 |
Additional metrics are available on the Open Targets Community.
New safety pharmacology data helps development of genetics-based approaches to understanding target safety
Safety liabilities associated with 33 targets have been extracted from a new publication by Brennan et al., who was until recently part of the Open Targets Safety Project.
The publication describes well-validated phenotypes associated with inhibition and activation of the 33 targets, primarily supported by clinical data and some preclinical data. The set of targets is based on safety panels routinely used in 18 pharmaceutical companies to screen new drug candidates for off-target activity.
One example is SLC6A1, a target with genetic data and a drug approved for epilepsy. The inhibition of this transporter increases GABA levels in the brain, and the safety events are derived from the same effects. SLC6A1 is an interesting example of relative severity: as an antiepileptic, the benefit of reducing seizures outweighs the side effects, but for anxiety, this cost-benefit analysis is less certain.
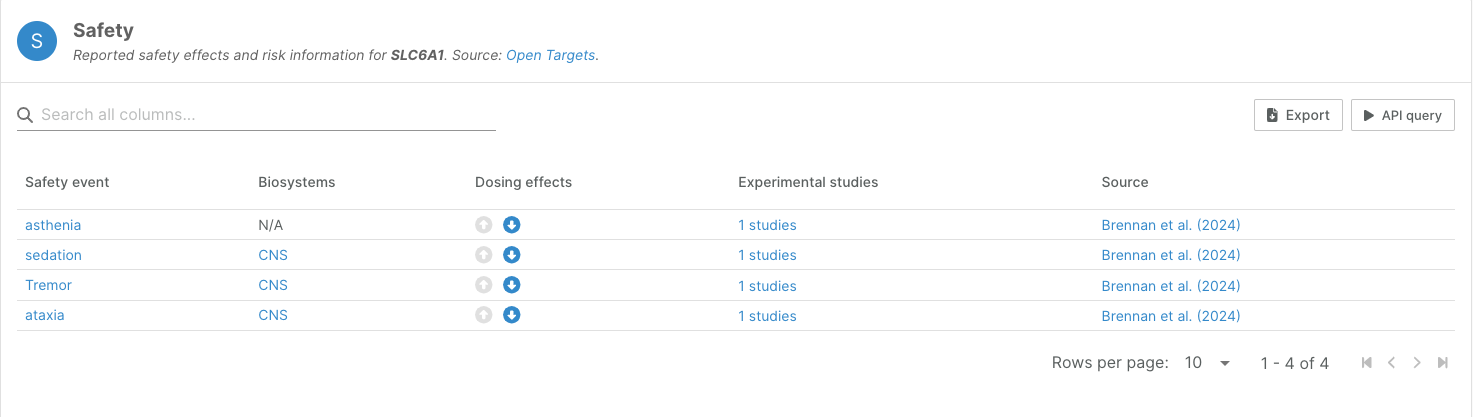
The new addition of 33 targets, of which 10 were not previously covered in the Open Targets Platform safety widget, provide a useful addition to the previously curated target-safety effect links, which cover 262 targets already in the Platform based on similar screening panels, plus another ~450 targets based on pharmacogenomics evidence.
FinnGen burden curation
FinnGen includes gene-based burden test results from collapsing loss of function variants, based on genotyping data from the Finnish population.
We have now included the analyses from FinnGen’s latest public release (R11) in the Platform as part of our Gene Burden evidence, a total of 368 evidence for 336 associations.
This is the first gene burden evidence for 316 associations, and in many cases, this is the first evidence of association.
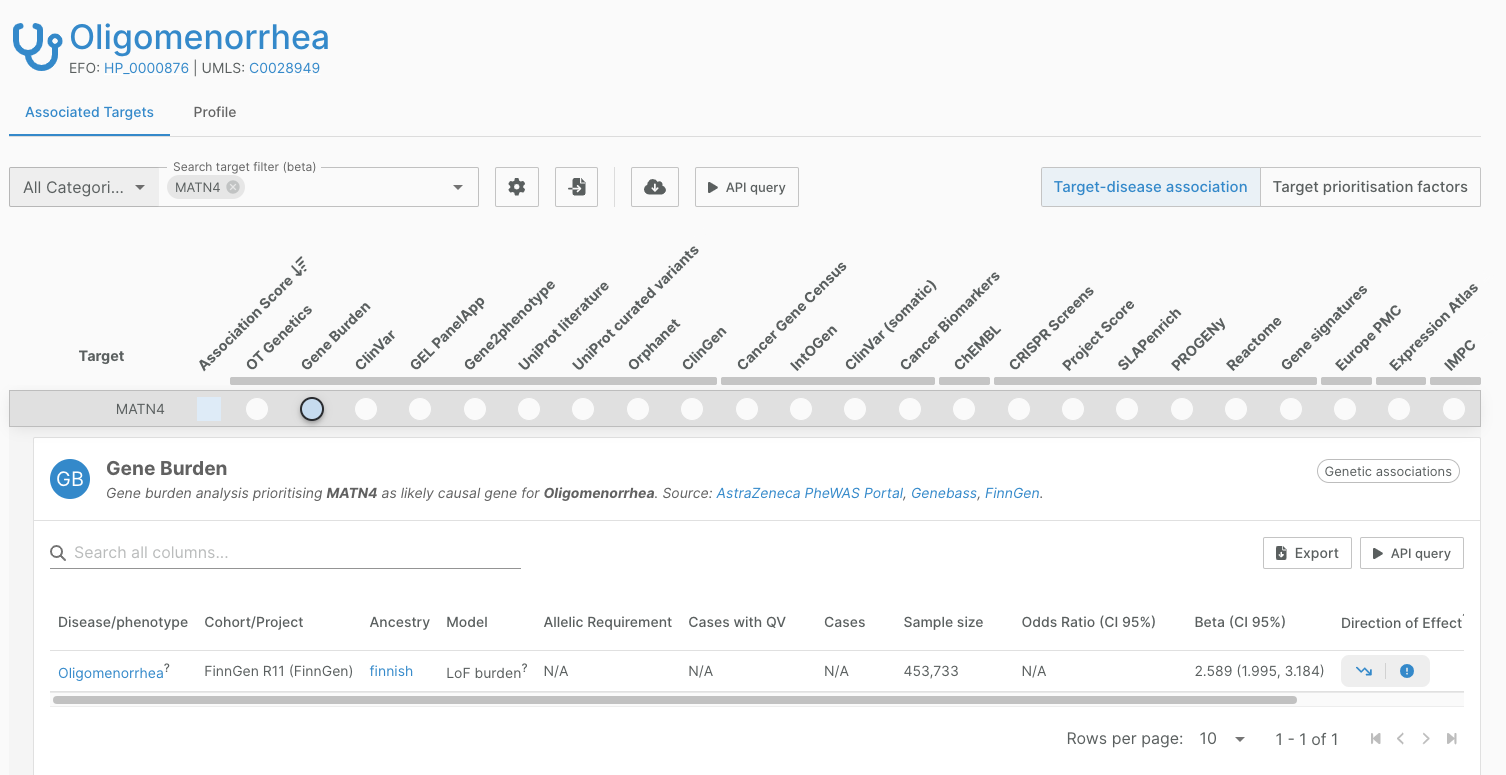
Find out more in the FinnGen documentation.
Filters for target-disease association evidence
When browsing associations in the Platform, you now have the ability to apply filters to the results. We have introduced this as a beta feature and are particularly interested in hearing your feedback.
This filtering capability complements the existing filtering by data type or data source.
A walkthrough of the new filtering feature
On a disease associations page, users can apply target-specific filters to get a customised list of associated targets.
This functionality allows you to explore sets of targets based on various structural, functional, and cellular characteristics. For example, targets can be filtered based on their subcellular location, biological process or pathway, target class, and tractability assessment, amongst other options.
Similarly, on a target page, users can apply disease-specific filters to narrow down the associations to a particular disease or therapeutic area.
Note that additional filters from the same category are added as OR filters. Filters from different categories are added as AND filters.
Please note, with the implementation of this feature, we have now deprecated our Classic associations page.
Open Targets data is available through Microsoft Azure
In another step towards the FAIRification of our platforms, Open Targets data is now available as an Open Dataset through Microsoft Azure. The 350 GB of data from both the Open Targets Platform and Open Targets Genetics are updated daily, and so should be synchronised with our releases.
We have a number of data access points for our data; browse our documentation to find out more.
OpenAI model used for literature summarisation has been updated
We have updated the OpenAI model used in our literature summarisation tool to GPT-4o-mini.
The literature summarisation tool provides natural language summaries of the target-disease evidence presented in a publication, as explained in our documentation.
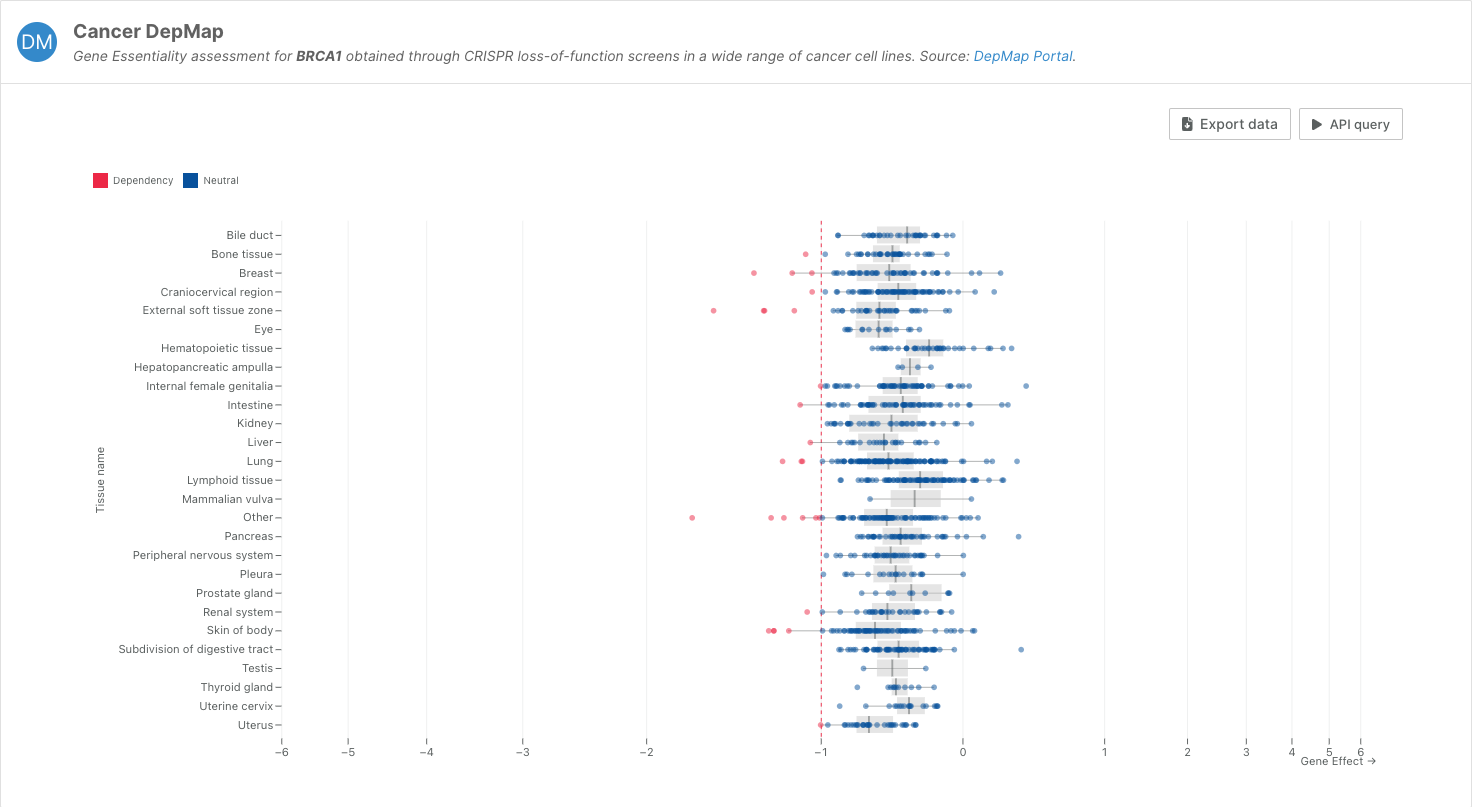
Gene essentiality data from DepMap has a new visualisation
The Cancer DepMap widget displays data from the DepMap portal, showing a gene essentiality assessment obtained through CRISPR loss-of-function screens in a wide range of cancer cell lines. Although in cancer, this experiment represents a good proxy of whether loss-of-functions are tolerated across a diverse set of tissues.
We have implemented a new visualisation for this data in the Platform, to better interpret the information presented. We've also added the option of exporting the data or seeing the API query for this widget.
As usual, please share any comments, questions, or suggestions on the Open Targets Community.
Written by the Open Targets team with contributions from Ines Smit, Safety Data Scientist and Informatician at ChEMBL.