Open Targets Platform 25.06 has been released!
The latest release of the Platform — 25.06 — is now available at platform.opentargets.org.
We hosted a walkthrough and Q&A session on LinkedIn (also available to watch on YouTube), in which the team showcased the new features and data in this release, and answered audience questions about the release and the Platform.
Key points
- The latest data from the GWAS Catalog brings in 36% more GWAS credible sets, most of which are from the VA Million Veteran Program study
- You can now view association evidence for a target’s interactors directly in our disease associations pages
- The Platform data downloads page is now powered by the Croissant metadata standard and easier to navigate
- We’ve updated the molecular structure viewer on target profile pages and added one to variant profile pages with AlphaMissense pathogenicity scores
- We have incorporated gene burden data from the Broad CVDI Human Disease Portal
- Our pharmacogenetics widgets contain additional annotation on the effect of the variants on drug availability
- Other improvements: search filters and EFO measurement terms
For the full list of updates, take a look at the release notes. For a list of key stats and metrics, see the Open Targets Community.
36% more credible sets from GWAS Catalog data
Thanks to the merge of Open Targets Genetics data and analysis pipelines into the Open Targets Platform, we can easily pull, finemap, and analyse GWAS data. Where possible, we fine-map and colocalise publication results curated and available through the GWAS Catalog.
The latest GWAS Catalog data in this release adds 36% more credible sets to the Platform from 211 publications.
One of these publications is a large multi-ancestry GWAS meta-analysis for osteoarthritis, combining 87 datasets. Published in Nature in April this year, Hatzikotoulas, Southam, Stefansdottir, Boer, McDonald, et al. integrated their GWAS findings with functional genomics data from relevant tissues, identifying 700 genes with high confidence of being involved in osteoarthritis, and eight biological processes key to the disease development, including circadian clock and glial cell functions.
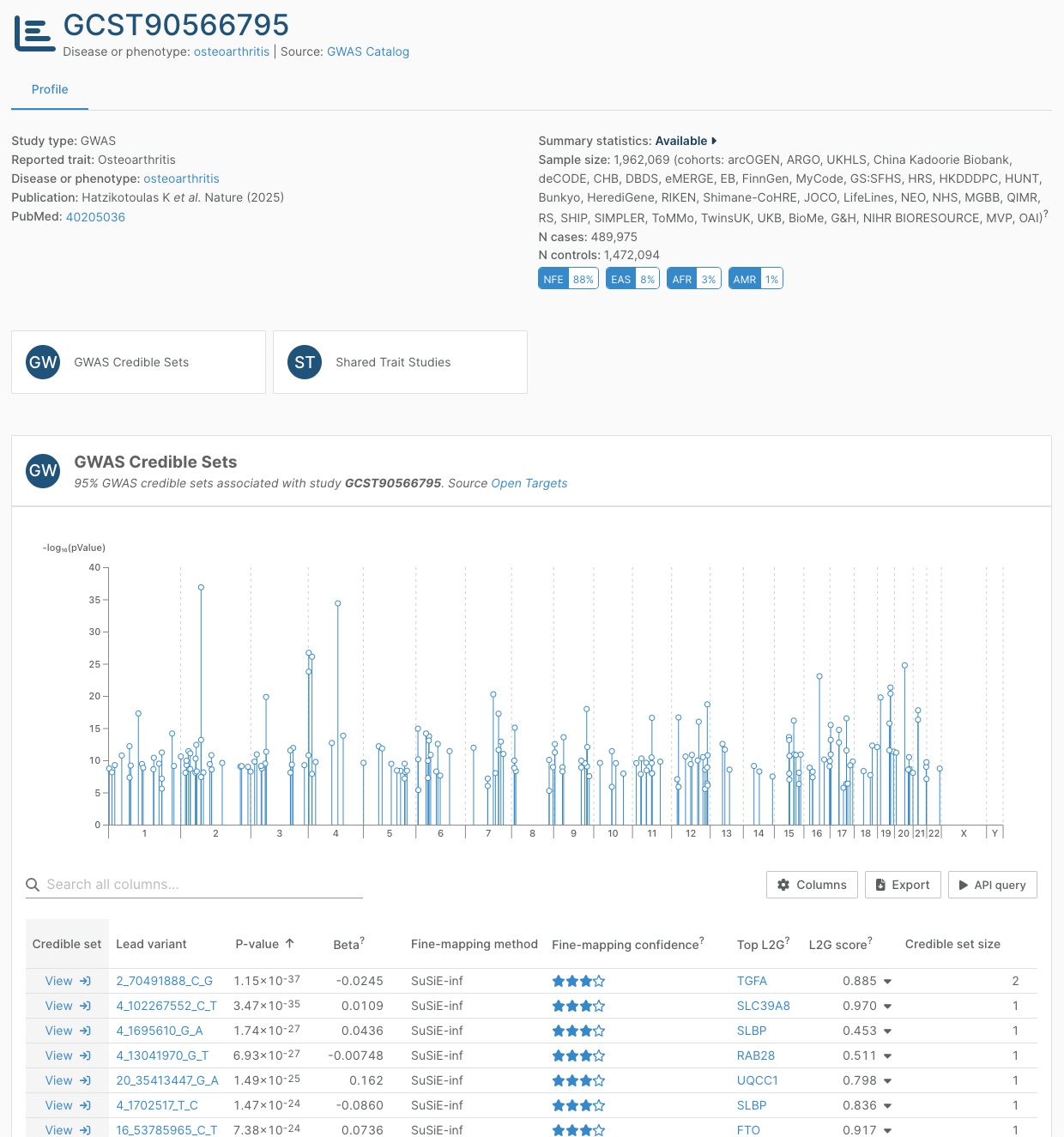
VA Million Veteran Program data
80% of new credible sets in this release derive from studies from the VA Million Veteran Program, an ongoing prospective cohort study and the largest multipopulation biobank to date. Verma, Huffman, Rodriguez, Conery, Liu et al. (2024) conducted Genome Wide Association Studies with over 635,000 participants, identifying more than 26,000 variant-trait associations across 1270 traits.
Our processing of the results from this publication contributed 172,000 credible sets that inform our Locus-to-Gene predictions. This included the first genetic evidence in the Platform for the association between ESR1 and osteoporosis.
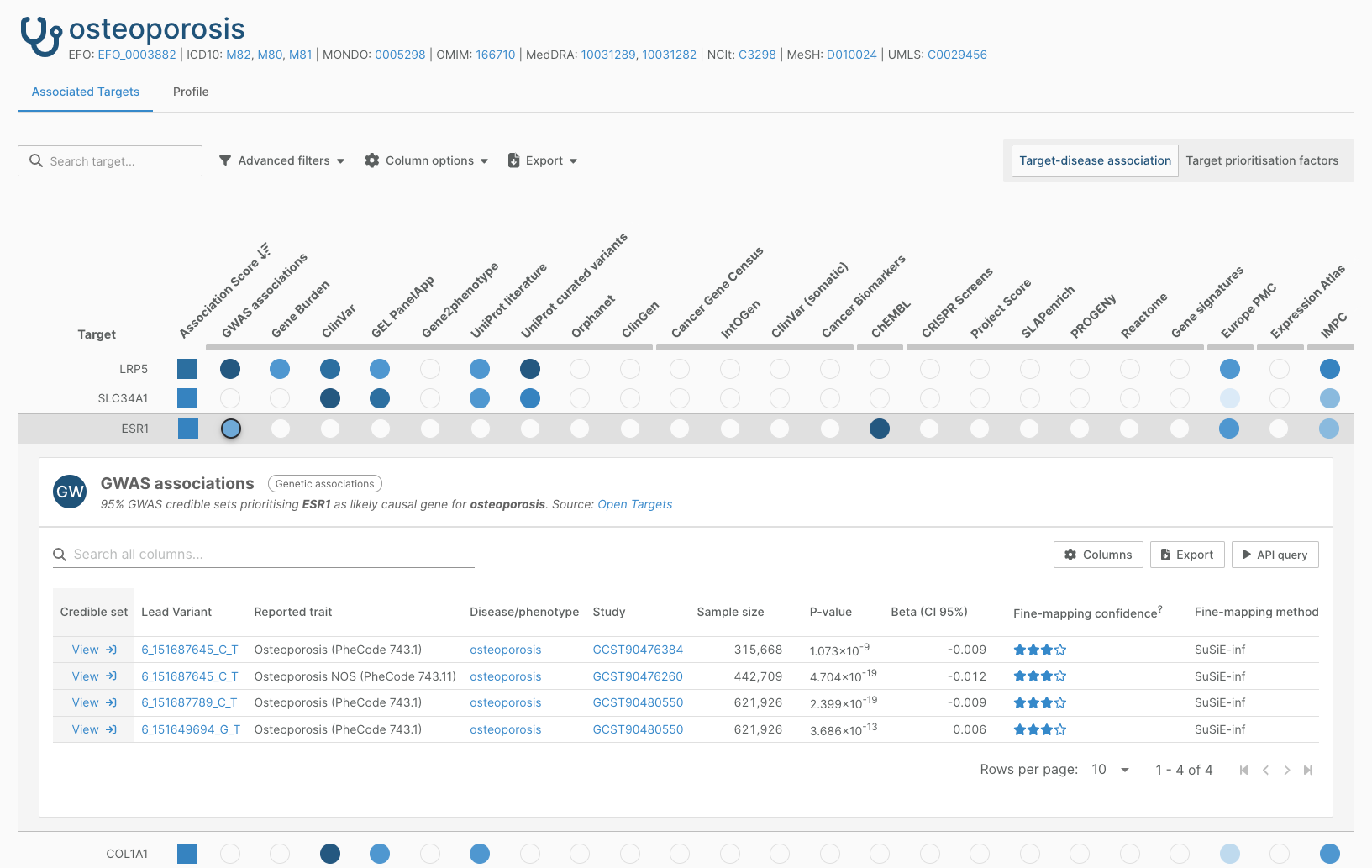
Changes to GWAS Catalog data in the Platform
We have made the decision to remove case-case studies from our GWAS data, for a total of 77 studies. Case-case studies are difficult to map to the correct disease, and therefore confound target-disease associations.
Nominating potential targets using target interactors
This release comes with a new Target Interactors view, which allows you to access association data for interactors of a given target, to quickly pinpoint other — potentially more favourable — targets, within the same network.
Target interactors can be viewed directly within the main ‘Associations on the Fly’ page. This is an option available for each target on a disease associations page; note that the interaction data is disease-agnostic.
Users can choose one of four sources of molecular interactors — IntAct (binary physical interactions), Reactome (pathway-based interactions), Signor (directional, causal interactions), and String (functional interactions) — and view the association evidence for the top scoring molecular interactors for that database. We’ve set default cutoff interactions scores which you can adjust.
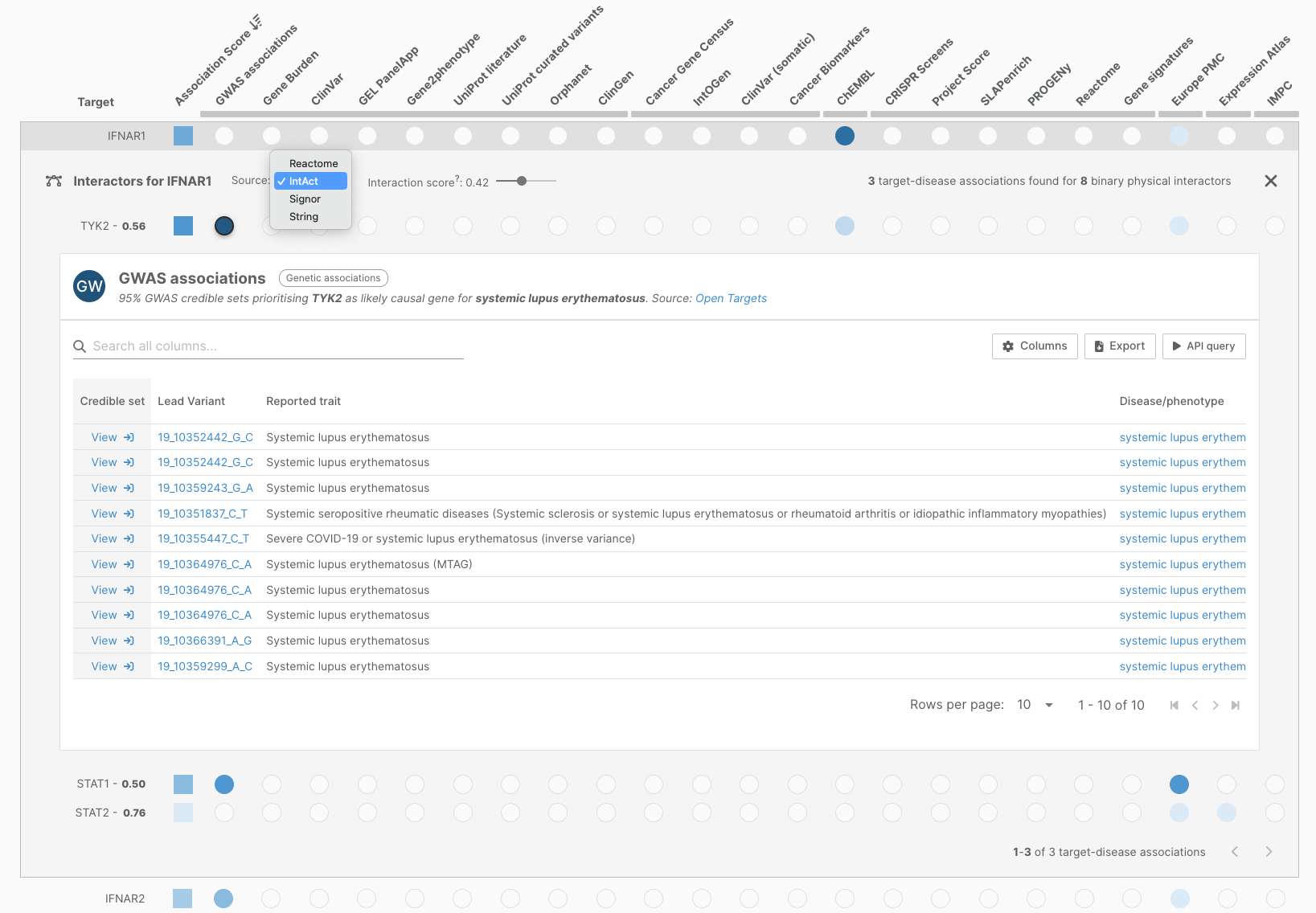
Find out more about target interactors in our documentation.
New data downloads page and Croissant
We have revamped our data downloads page, making it easier for you to find the dataset you need. In addition to the description, each of the 37 datasets now features a data category tag, to make it easier for you to filter. You can view the schema for each dataset, including column descriptions, primary and foreign keys, and the data access options.
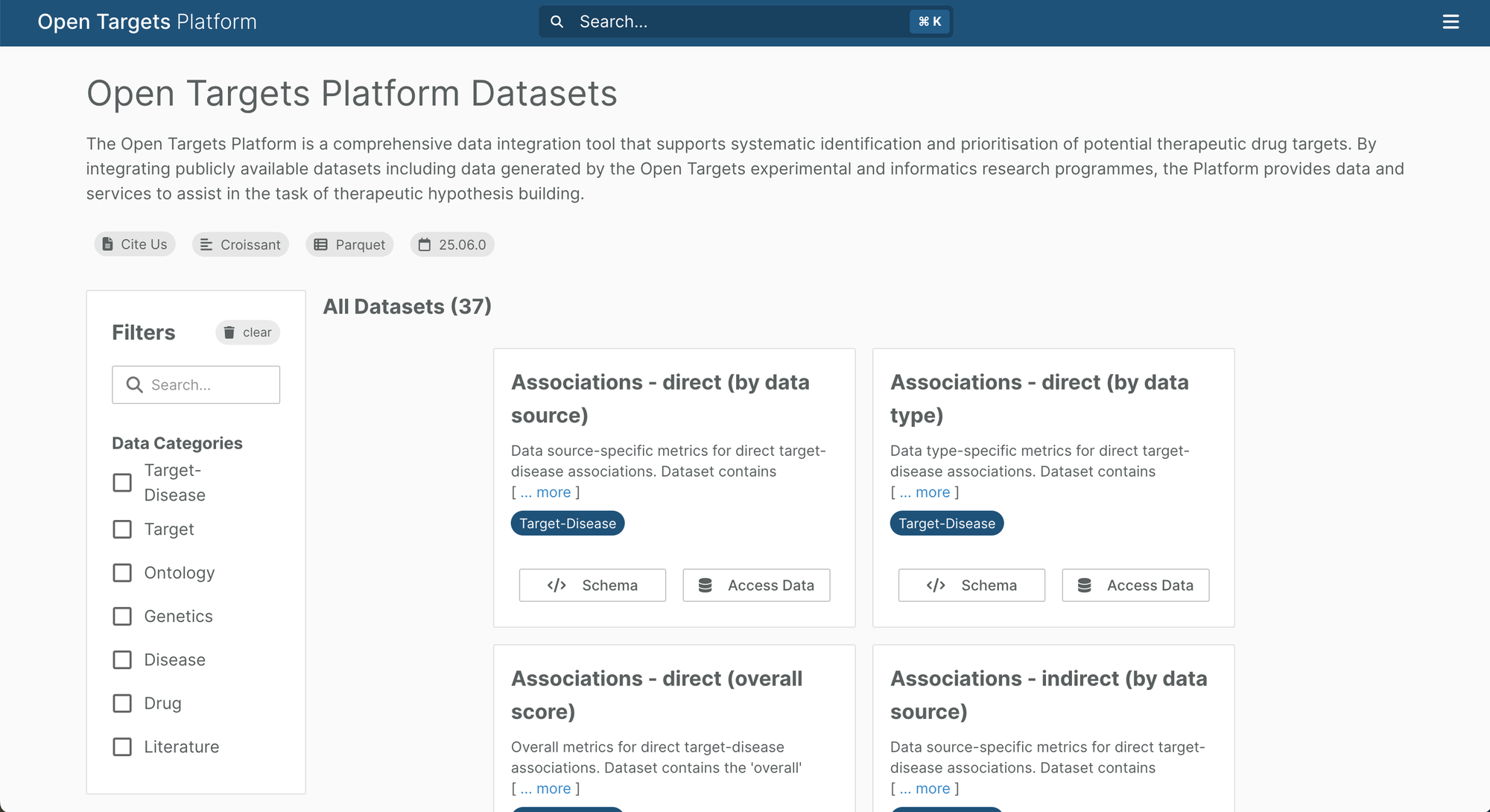
Croissant
We have described our data following the Croissant metadata standard format, based on JSON-LD, developed by ML-Commons. The Croissant format simplifies how data is used by ML models, and will make Open Targets Platform data discoverable and FAIRer.
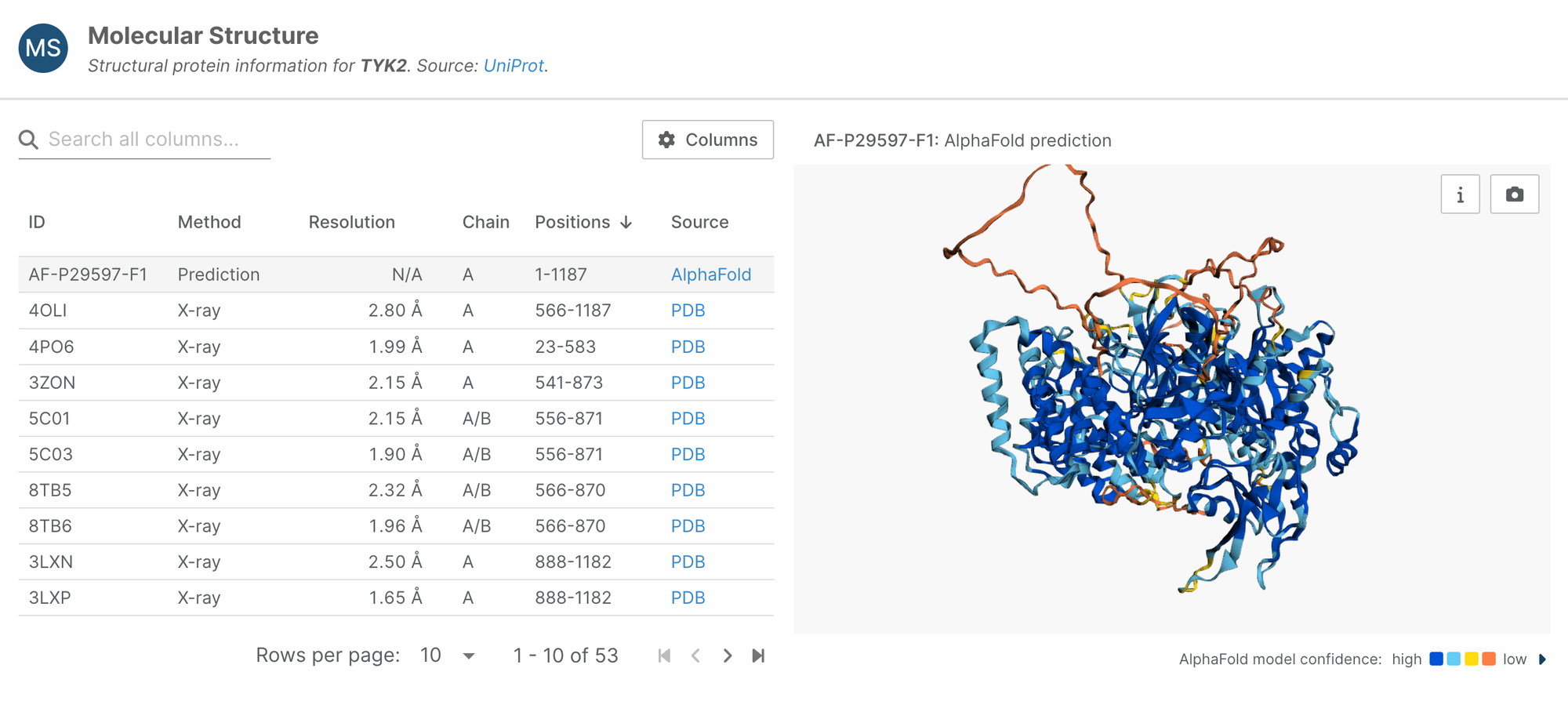
Molecular structure viewers
We have updated the Molecular Structure viewer on target profile pages, and added a version of the viewer on missense variant pages, which indicates the location of the variant in the AlphaFold model.
On target pages, the Molecular Structure viewer allows you to browse structural protein information from Uniprot, and compare structures derived from different methods, including AlphaFold predictions, X-ray, EM and NMR.
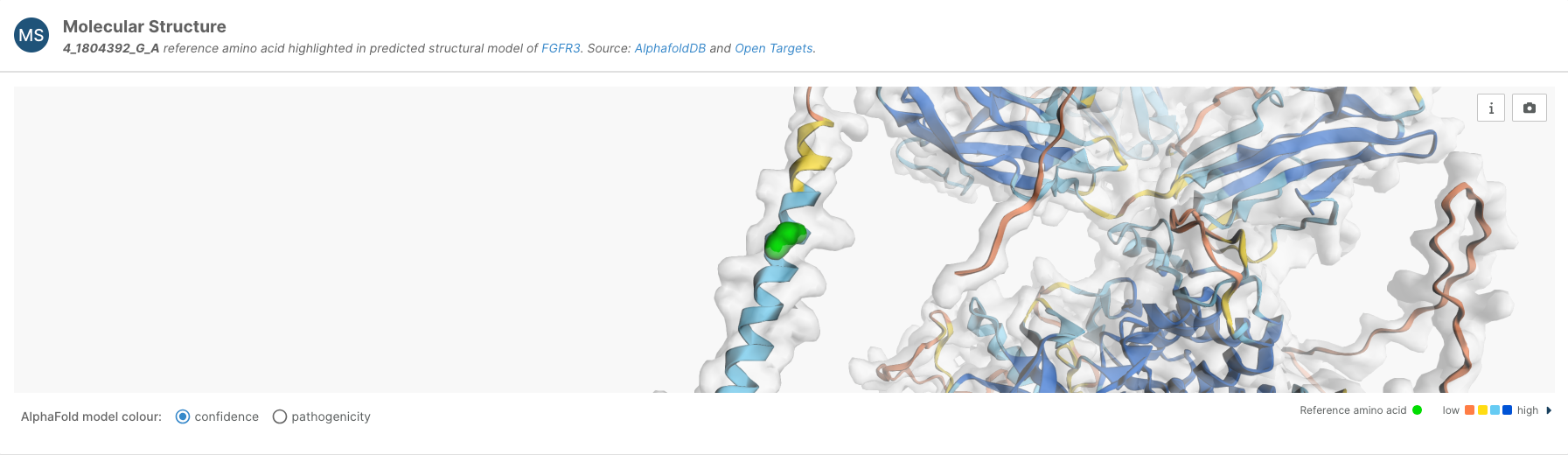
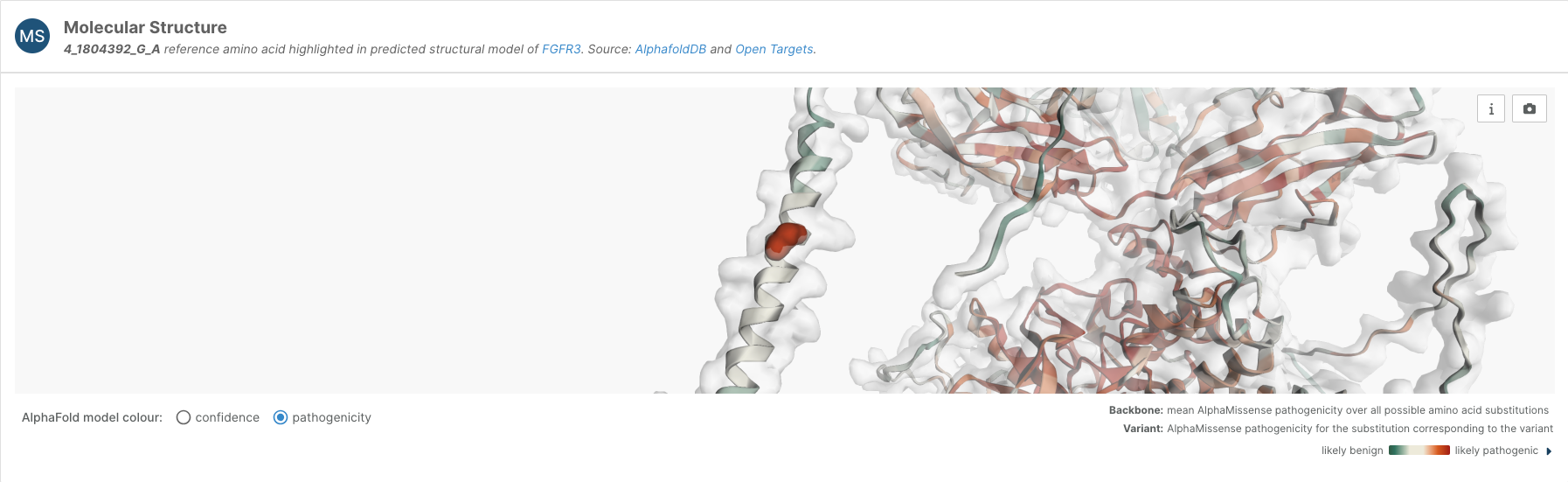
For predicted missense variants, we have included a Molecular Structure viewer on the variant page that locates the variant in the AlphaFold structure. Moreover, users have the option to switch to a pathogenicity view, which shows the AlphaMissense pathogenicity for the substitution corresponding to the variant, and the average AlphaMissense pathogenicity score across all possible amino acid substitutions at other positions.
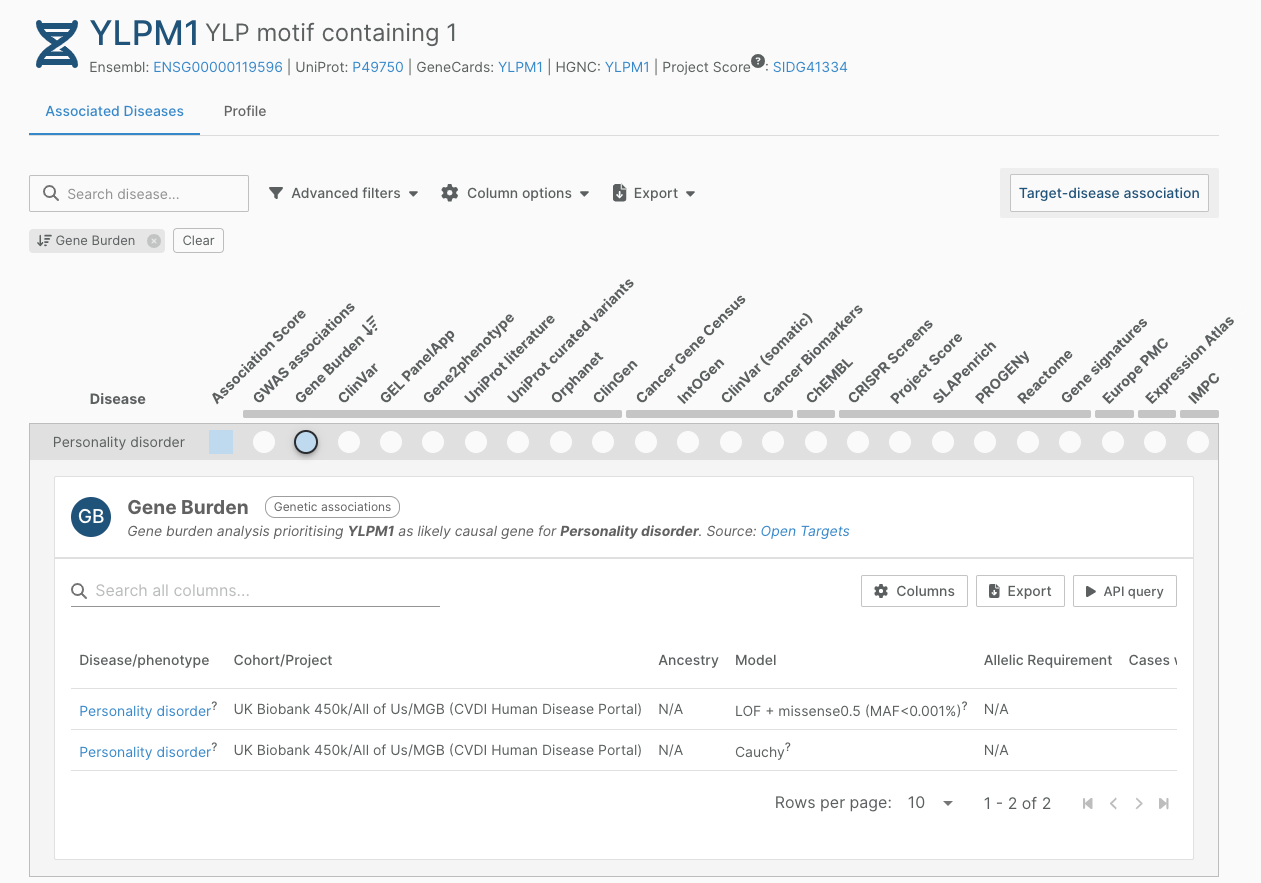
Burden evidence from the Broad CVDI Human Disease Portal
We have incorporated data from the Broad CVDI Human Disease Portal into our gene burden analyses. Our Gene Burden datasource incorporates results from the aggregation of rare and ultra-rare variants at the gene-level.
The Portal features pan-ancestry sequencing data from three large biobanks: the UK Biobank, All of Us, and the Mass General Brigham Biobank. Jurgens, Wang, et al. (2024) performed gene-based rare variant testing across almost 750,000 individuals, including more than 155,000 with non-European ancestry, and identified 363 significant associations for 123 genes in 165 diseases, including some novel associations.
In addition to the independent gene burden analyses performed on each cohort, the team also meta-analysed rare variation across ancestries, correcting for overlap in samples between ancestries. This work yielded new associations, but also identified key genes in the phenome of human diseases. These genes are highly pleiotropic and are associated with large effect sizes.
We have mapped the study’s disease terms to our ontology, and processed all burden results from this study that analysed all three cohorts, with different masks and filtered based on the statistical method. This means that certain associations are supported by multiple evidences from this study, if the association was found statistically significant in multiple statistical methods. In total, we have included 1,530 evidence strings for 520 targets/disease pairs in the Platform.
Directionality annotations for pharmacogenetics data
Pharmacogenetics widgets on the variant, target, and drug profile pages now have an additional Directionality column. Where information is available, this provides an indication of how the variant affects drug response.
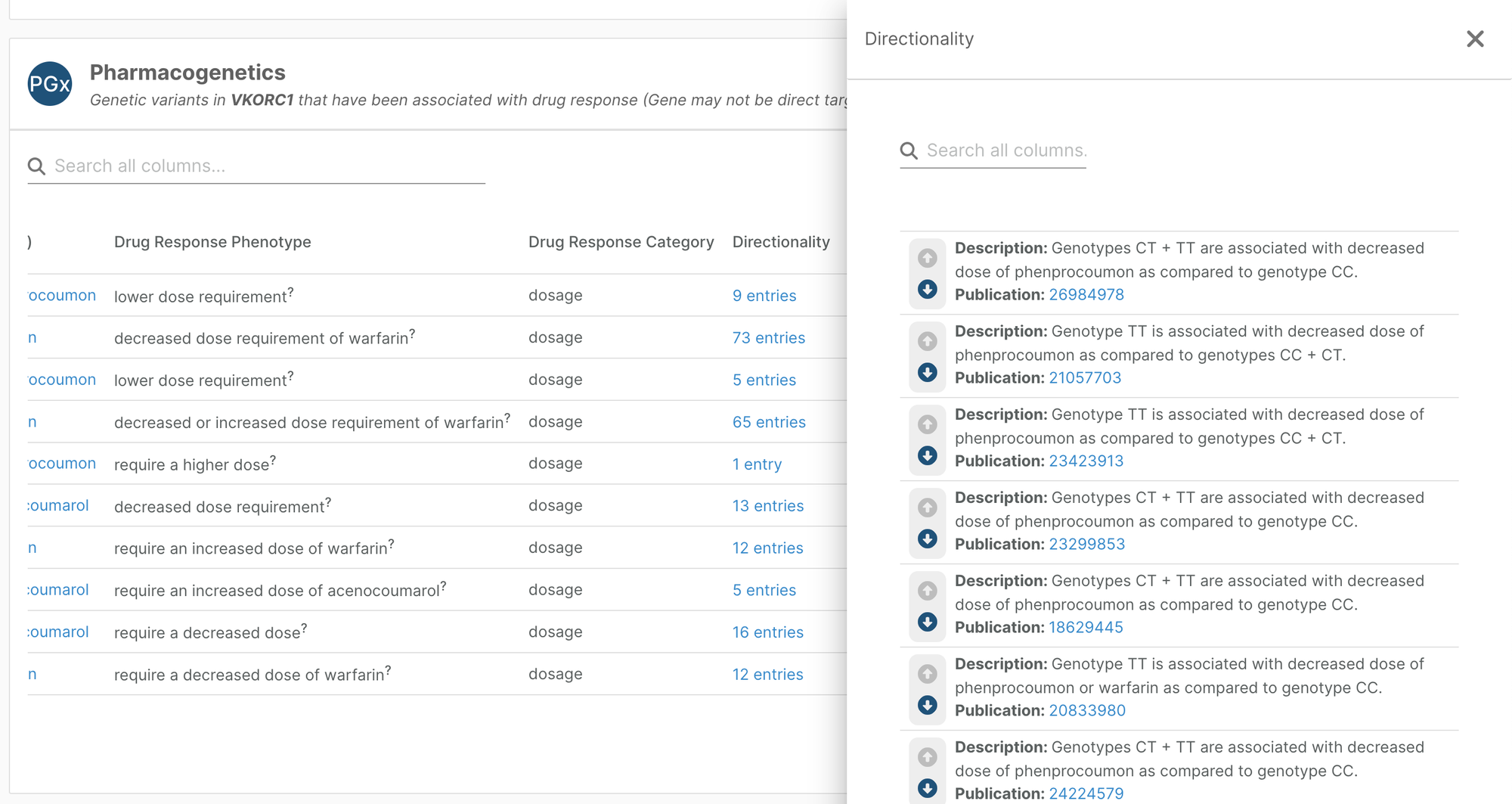
The European Variation Archive team has been working to integrate more detailed variant-level annotations from PharmGKB and mapping them to clinical annotations. We now have additional information for 67% of all pharmacogenetics evidence in the Platform.
With this additional annotation, you can quickly see whether a particular genotype for the variant is associated with a requirement for a decrease or increase in the drug dosage (as pictured), confers an increase or decrease in enzyme activity, or an increased or decreased risk/severity of drug toxicity, compared to other genotypes. Also provided are how many studies have information on this relationship, and how concordant they are. There are links to each publication so that you can find out more.
Improved search functionality
We have strengthened our search functionality with performance optimisations and additional filtering capabilities. For example, when you search for a term in the Platform, you now have the option of filtering by entity type.
Measurement EFO terms
The latest Experimental Factor Ontology (EFO) replaced measurement terms with terms from the Ontology of Biological Attributes (OBA), and this is now reflected in the Platform, with downstream consequences on GWAS credible sets and association evidence from Europe PMC.
As usual, please share any comments, questions, or suggestions on the Open Targets Community, and join our walkthrough and Q&A session on LinkedIn!