Everything you need to know about the new GWAS Catalog
Genetic evidence could double the rate of success in drug targets identification - so the scientific community predicts. With this in mind, it is crucial for Open Targets to be able to feed as many SNP-trait associations as possible into its pipeline for systematic target identification and validation.
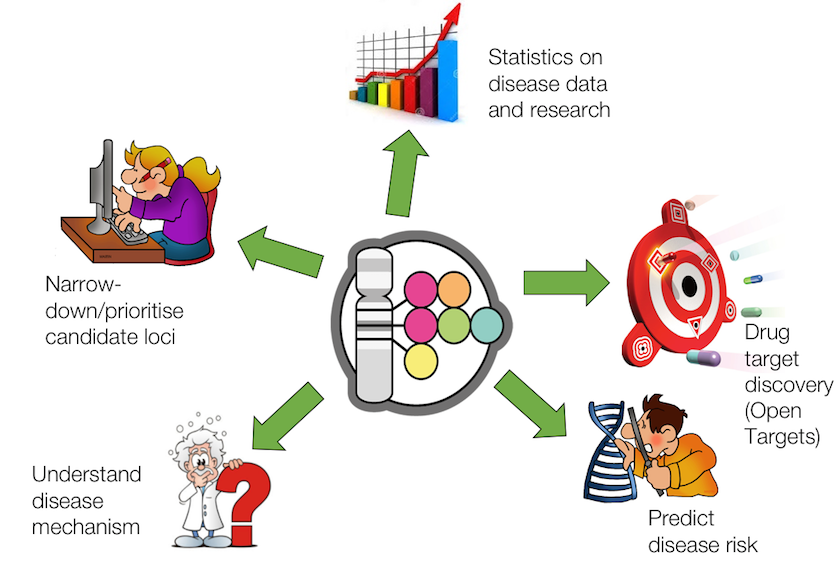
The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog, an awesome public resource of human genotype-phenotype associations from published GWAS analyses, is one of the data sources for manually curated genetic evidence for the Open Targets Platform. The GWAS Catalog data is widely used to prioritise new candidate loci, predict disease risk and understand disease mechanisms, with a number of users and applications that is always increasing.
New and expanded GWAS Catalog to improve target identification
I am happy to announce an expansion of the GWAS Catalog scientific scope to host non genome-wide studies. During its first 10 years of life, in fact, the GWAS Catalog has only included array studies with genome-wide coverage, therefore curation of exome and targeted array studies were outside its scientific scope. These data are however valuable to Open Targets’ scientific goals of target identification and prioritisation, so much so they decided to invest in a new project aiming to expand the scope of the Catalog to include targeted arrays, such as MetaboChip, ImmunoChip, and Exome array. The new GWAS will now allow variants associated with immunologic, metabolic and oncologic phenotypes to be included in the Open Targets Platform for the expansion of target identification and selection in these traits.
Selecting and curating non-genome-wide array studies
As a first step, Open Targets selected almost 60 publications for inclusion in the GWAS Catalog. I then extracted a total of 120 new independent association studies and 823 SNP-trait associations from these publications. These are impressive numbers, and give you an idea of how many studies and SNP-trait associations (and potential targets) we were missing by not including targeted array studies in the GWAS Catalog!
The final step for me to do was to map all these traits, diseases and phenotypes to EFO terms, the ontology used by Open Targets to describe its diseases.
Modifying the GWAS Catalog user interface
The GWAS Catalog team have changed the way the user interface works to support searching, displaying, filtering and download of targeted and exome array studies. Try it out using "celiac disease", for example. The interface will now give you:
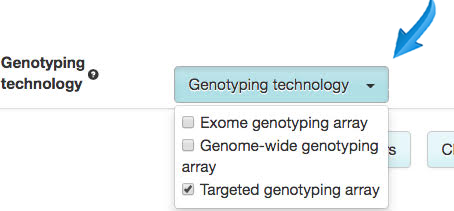
- Drop-down filter by genotyping technology to help you focus on your favourite array
- Small "target" icon (designed for us by the EMBL-EBI media team. Thanks for that!) in the study accession number column for all targeted array studies prioritised by Open Targets

- New "genotyping technology" shown for study, e.g. genome-wide genotyping array, exome-wide genotyping array or targeted genotyping array with an optional field for additional array information, for example ImmunoChip or MetaboChip

Stay tuned!
This is an important milestone for Open Targets and the GWAS Catalog, and a lot more is yet to come. The next step for the collaboration between GWAS and Open Targets will be to develop a comprehensive database of all available GWAS full summary statistics stored in a common format and harmonised across studies to enable searching, easy comparison and downstream analysis. This effort will generate more comprehensive new raw genetic data accessible by the entire research community through the GWAS Catalog, the Open Targets Platform and additional resources the Open Targets team are working on.